王牌战斗机无限金币最新版
82.23MB · 2025-12-01
本文介绍GraphQL中的Authenication和Authorication
参考:
Authenication 和 Authorication 的概念十分容易混淆,两者的定义如下:
提供用户的authenication有多种方式,包括HTTP header和JSON web token。
下面给出一个创建Authenication的示例
分别创建一个用户信息的type,并定义创建用户和登录的方法
type AuthPayload { token: String! name: String!}input UserCreateInput { name: String! password: String!}type Mutation { createUser(data: UserCreateInput): String login(data: UserCreateInput): AuthPayload logout(data: UserCreateInput, param: Int!): Int}通常情况下,用户在用前端创建用户时,会传入用户名和密码,后端不会直接保存用户密码,而是将用户信息加密为webtoken储存起来,而login的情况下,也是会将用户用户名和密码的信息与weebtoken进行比对。
可以在context中,设置一个用户组缓存来储存数据,同样适用于将用户信息储存于数据库或云端。
const resolver = { Mutation: { createUser: async (parent: any, args: any, ctx: any, info: any) => { if (args.data.password.length < 8) { throw new Error('Password must be 8 characters or longer.') } const password = await bcrypt.hash(args.data.password, 10); const id = uuidv4(); const token = jwt.sign({ userId: id }, 'password'); ctx.users.push({ id, name: args.data.name, password, token }); return token; }, login: async (parent: any, args: any, ctx: any, info: any) => { const user = ctx.users.find(u => u.name === args.data.name); if (!user) throw Error('User not exist'); const isMatch = await bcrypt.compare(args.data.password, user.password); if (!isMatch) throw new Error('Password mismatch'); return { name: user.name, token: user.token ? user.token : jwt.sign({ userId: user.id }, 'password'), } }, }}用上述步骤执行完Authentication的操作以后,需要验证用户操作函数是否有权限只需要在相应方法的Resolver中进行验证即可,调用Query或Mutation可以在Header中添加一个由后端返回给前端的token,示例如下:
后端:
const getUserId = (request) => { const token = request.headers.authorization; if (!token) { throw new Error('Authentication required') } const decoded = jwt.verify(token, 'password') return decoded.userId}const resolver = { Mutation: { callFunction: async (parent: any, args: any, ctx: any, info: any) => { const id = getUserId(ctx.request); if (!id) throw Error('ID not exist'); // Do operation } }}在Apollo GraphQL中可以在前端的header加一个authorication的字段,输入token:
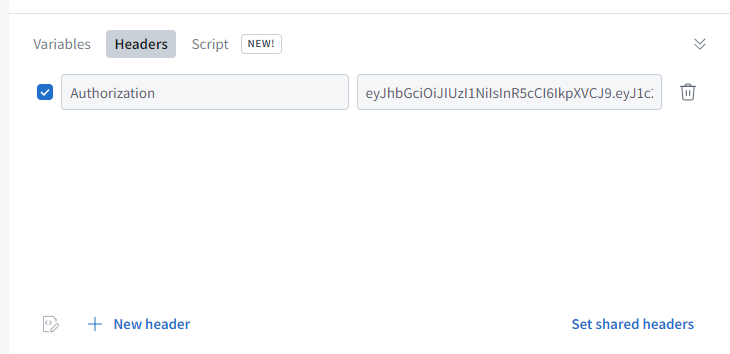
前端可以在创建Apollo GraohQL Module时,创建一个MidWare包含我们的header:
const authMiddleware = new ApolloLink((operation: any, forward: any) => { operation.setContext({ headers: new HttpHeaders().set( "Authorization", "eyJhbGciOiJIUzI1NiIsInR5cCI6IkpXVCJ9..." //Token ), }); return forward(operation);});export function createApollo(httpLink: HttpLink): ApolloClientOptions<any> { return { link: httpLink.create({uri}), cache: new InMemoryCache(), };}export function createApolloWithAuth(httpLink: HttpLink): ApolloClientOptions<any> { return { link: from([ authMiddleware, httpLink.create({ uri, }), ]), cache: new InMemoryCache(), };}