cad看图王手机版正式版
94.06MB · 2025-10-29
<a>标签引发的思考<!-- 2005年的典型网站导航 -->
<nav>
<a href="index.html">首页</a>
<a href="about.html">关于我们</a>
<a href="contact.html">联系我们</a>
</nav>
每个前端开发者都经历过的痛苦:点击链接→白屏闪烁→重新加载...
# 文件结构(每个页面都是独立的HTML)
public/
├── index.html # 包含导航+首页内容
├── about.html # 包含导航+关于内容
└── contact.html # 包含导航+联系内容
// 浏览器默认行为
document.querySelector('a').addEventListener('click', function(e) {
// 1. 停止当前页面执行
// 2. 卸载所有JavaScript
// 3. 发起新页面请求
// 4. 重新解析HTML/CSS/JS
// 5. 从头开始渲染
});
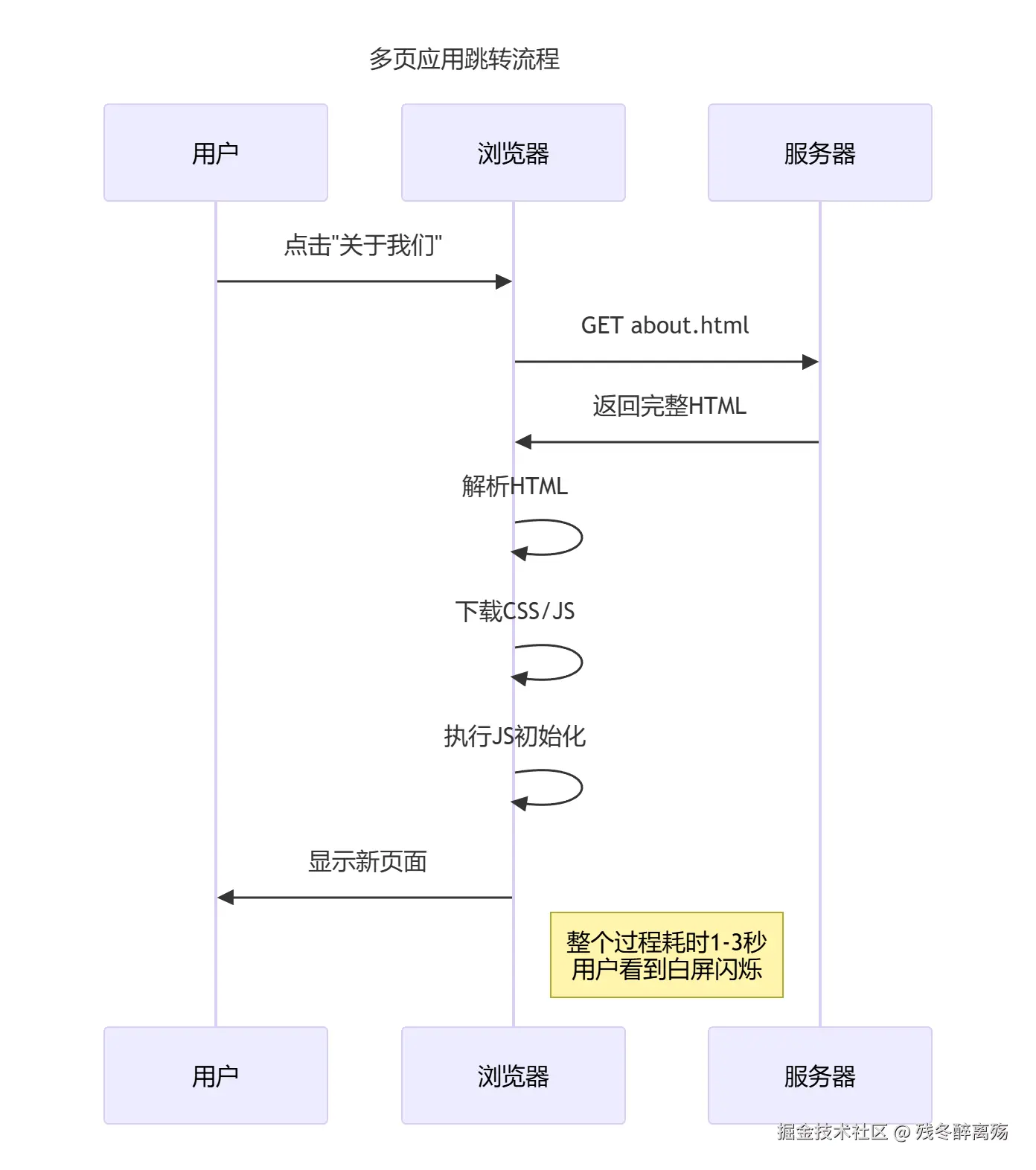 #### 1.4 多页应用的四大痛点
#### 1.4 多页应用的四大痛点
痛点1:资源重复加载
<!-- 每个HTML都包含相同的资源 -->
<head>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="styles.css"> <!-- 重复下载 -->
<script src="jquery.js"></script> <!-- 重复执行 -->
</head>
痛点2:状态无法保持
// 在index.html中
let formData = { name: '张三', progress: 50% };
// 跳转到about.html后:数据丢失!
痛点3:交互体验割裂
痛点4:开发效率低下
<!-- 每个页面都要重复写导航 -->
<nav>...</nav>
<!-- 修改导航需要更新所有HTML文件 -->
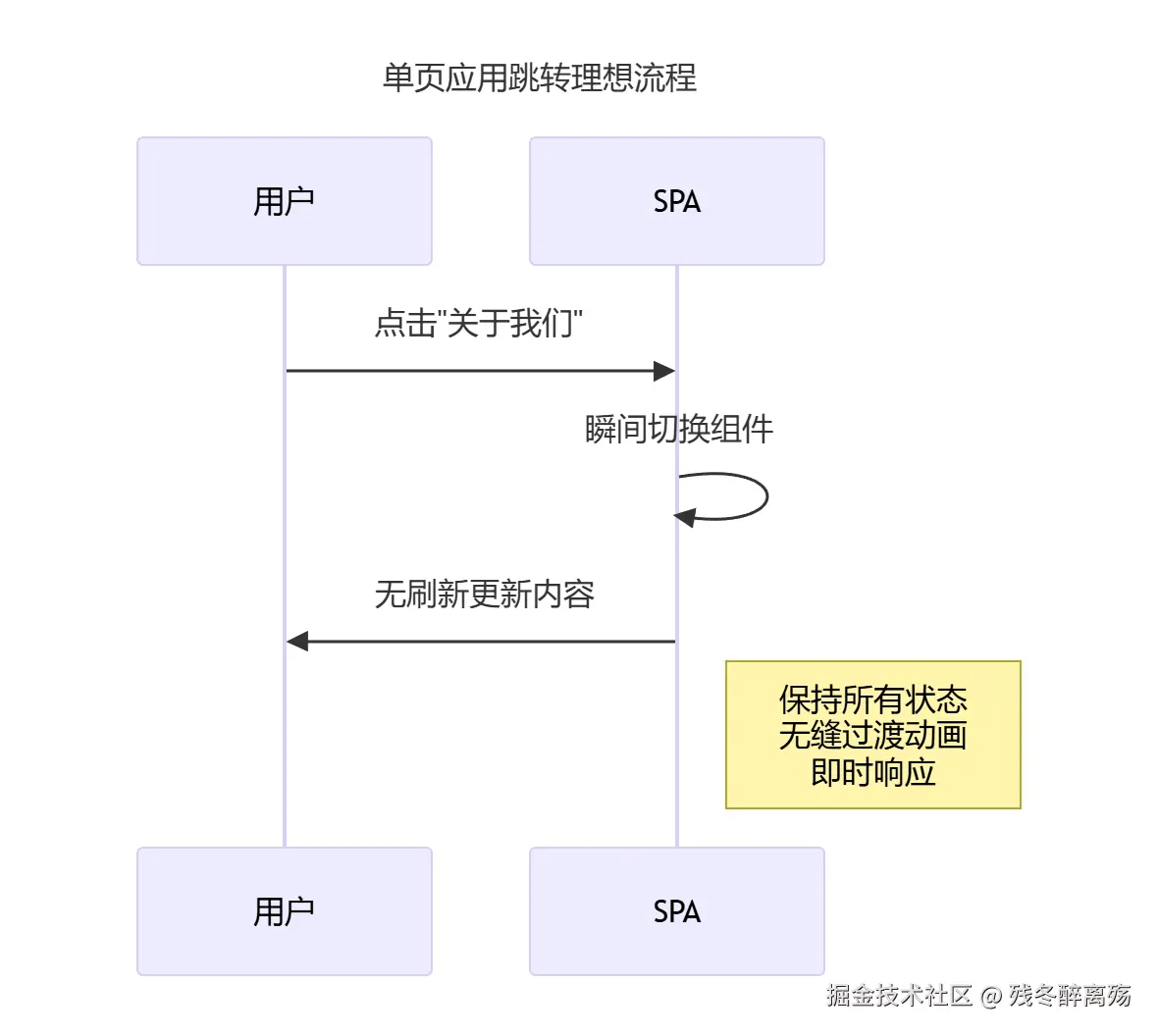
# 单页应用文件结构
public/
└── index.html # 唯一入口
src/
├── app.js # 应用主逻辑
├── components/ # 可切换的组件
│ ├── Home.js
│ ├── About.js
│ └── Contact.js
└── router.js # 前端路由
// 尝试直接跳转
function goToAboutPage() {
window.location.href = '/about'; // 还是会整页刷新!
}
核心问题:浏览器设计初衷是文档查看器,默认认为URL变化=请求新文档。
某个深夜,Gmail团队发现:
<!-- 传统锚点跳转 -->
<a href="#section1">跳转到第一节</a>
<!-- 点击后URL变成:current.html#section1 -->
<!-- 神奇的是:页面不刷新,只是滚动位置变化! -->
// 测试发现:
window.location.hash = '#test'; // 修改hash不会刷新页面!
// 而且可以监听变化:
window.addEventListener('hashchange', function() {
console.log('Hash变了!可以在这里做点什么...');
});
原始用途:
// 锚点:页面内跳转
<a href="#chapter1">第一章</a>
// 浏览器:滚动到id="chapter1"的元素
hack用法:
// 前端路由:应用内跳转
<a href="#/about">关于我们</a>
// 前端JS:动态加载About组件并渲染
class HashRouter {
constructor() {
// 监听URL的hash变化
window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => {
const path = this.getPathFromHash();
this.renderComponent(path);
});
}
navigateTo(path) {
// 通过修改hash实现无刷新跳转
window.location.hash = '#/' + path;
}
getPathFromHash() {
return window.location.hash.slice(2) || 'home'; // 去掉#/
}
renderComponent(path) {
// 根据路径显示不同内容
document.getElementById('app').innerHTML =
`当前页面: ${path}`;
}
}
// 使用示例
const router = new HashRouter();
# 典型的Hash模式URL
http://example.com/#/home
http://example.com/#/products/42
http://example.com/#/user/profile
// 无需服务器配置
// 完美兼容IE6+
// 实现成本低
# 1. URL丑陋
http://site.com/#/about vs http://site.com/about
# 2. SEO不友好
搜索引擎早期忽略#后的内容
# 3. 语义奇怪
#/about 看起来像"关于页的锚点"而非独立页面
开发者的心声:“我们像是在用胶带修补一个设计缺陷...”
WHATWG(Web超文本应用技术工作组)意识到:
于是推出了:
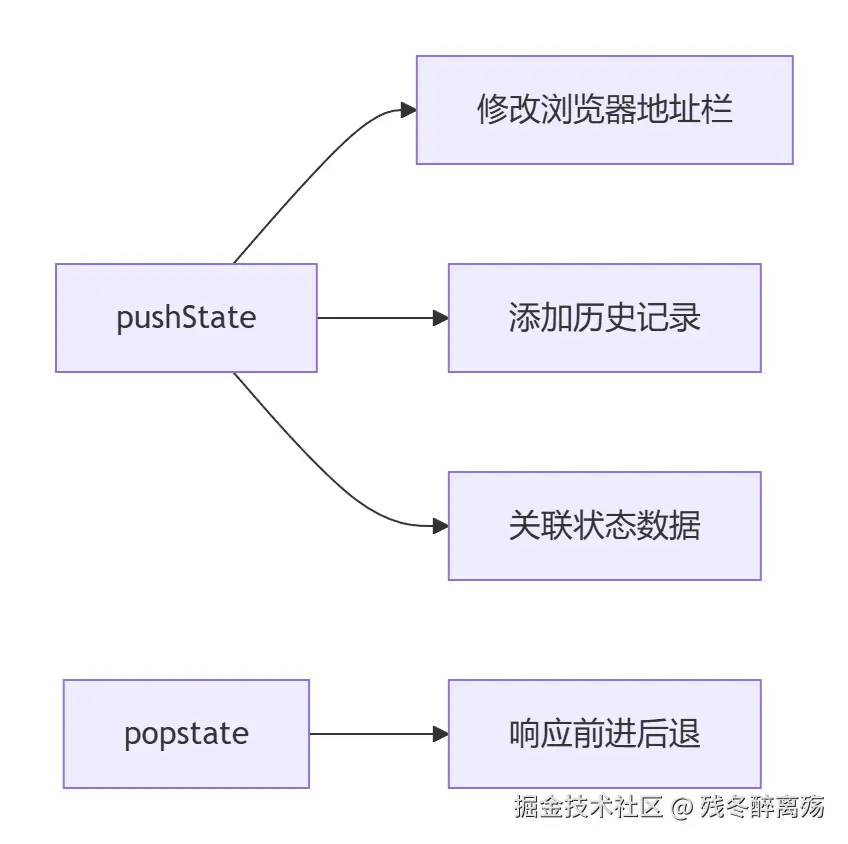
// 革命性的API
history.pushState(stateObject, title, url);
history.replaceState(stateObject, title, url);
// 对应的监听事件
window.addEventListener('popstate', handler);
// 可以无刷新修改完整URL!
history.pushState({page: 1}, "Page 1", "/page1");
// 结果:URL变成 http://example.com/page1
// 且:不刷新页面!不请求服务器!
关键突破:
当用户直接访问SPA的路由地址(如/about)时,服务器默认会查找about.html,但SPA只有一个index.html,导致404错误。
让所有路径请求都返回index.html,由前端路由处理页面渲染:
location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.html; # 最终返回index.html
}
| 模式 | URL示例 | 服务器请求路径 | 是否需要配置 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hash | /#/about | / | 不需要 |
| History | /about | /about | 需要 |
#后的内容不会发送到服务器,天然兼容| 特性 | Hash模式 | History模式 |
|---|---|---|
| URL美观度 | 带# | 原生URL |
| 服务器要求 | 无需配置 | 需特殊处理 |
| 兼容性 | IE6+ | IE10+ |
| SEO友好 | 较差 | 较好 |
timeline
title 路由模式演进时间线
2004 : Gmail使用Hash路由
2010 : HTML5 History API发布
2012-2015 : 两种模式并存过渡
2016+ : History模式成为主流
// 现代项目首选
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history', // 优雅!
routes: [...]
});
// 需要兼容旧浏览器时
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'hash', // 稳妥!
routes: [...]
});