最终王冠手游
1.2GB · 2025-12-07
本章对C++程序的基本结构做一概述,并预览后面将介绍的主题,如函数和类。
// myfirst.cpp--displays a message
#include <iostream> // a PREPROCESSOR directive
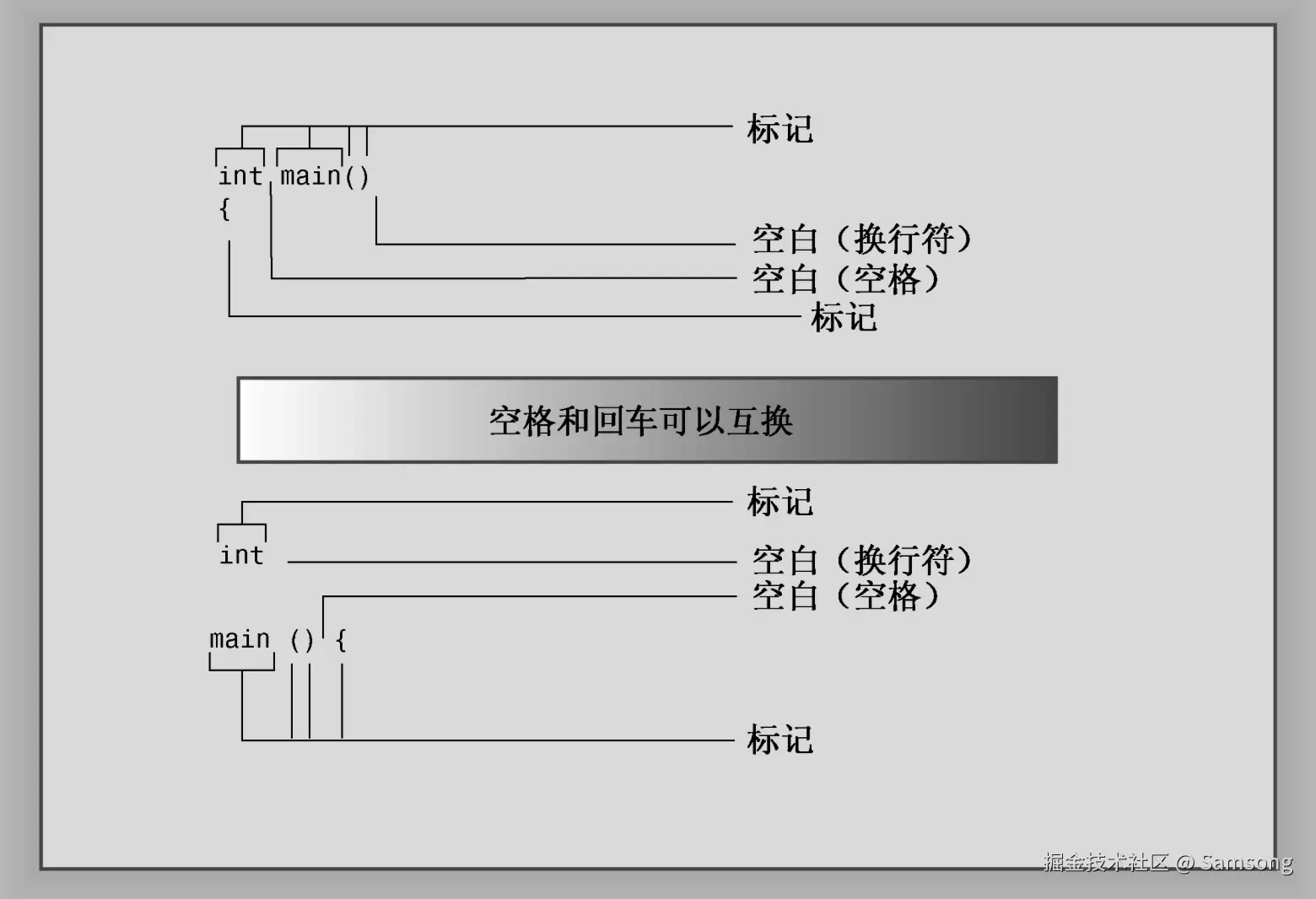
int main() // function header
{ // start of function body
using namespace std; // make definitions visible
cout << "Come up and C++ me some time."; // message
cout << endl; // start a new line
cout << "You won't regret it!" << endl; // more output
// If the output window closes before you can read it,
// add the following code:
// cout << "Press any key to continue." <<endl;
// cin.get();
return 0; // terminate main()
} // end of function body
示例代码包含下述元素
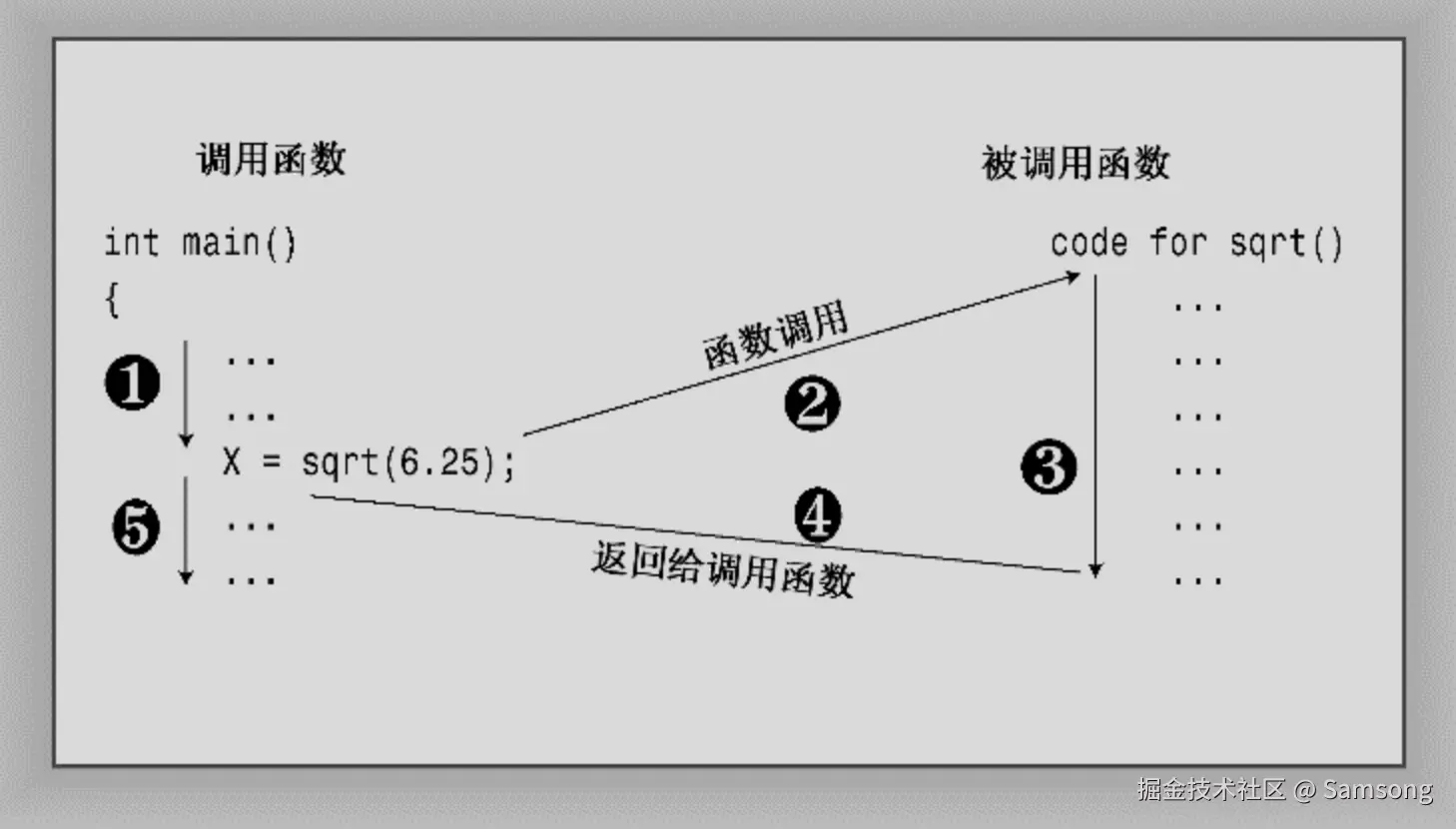
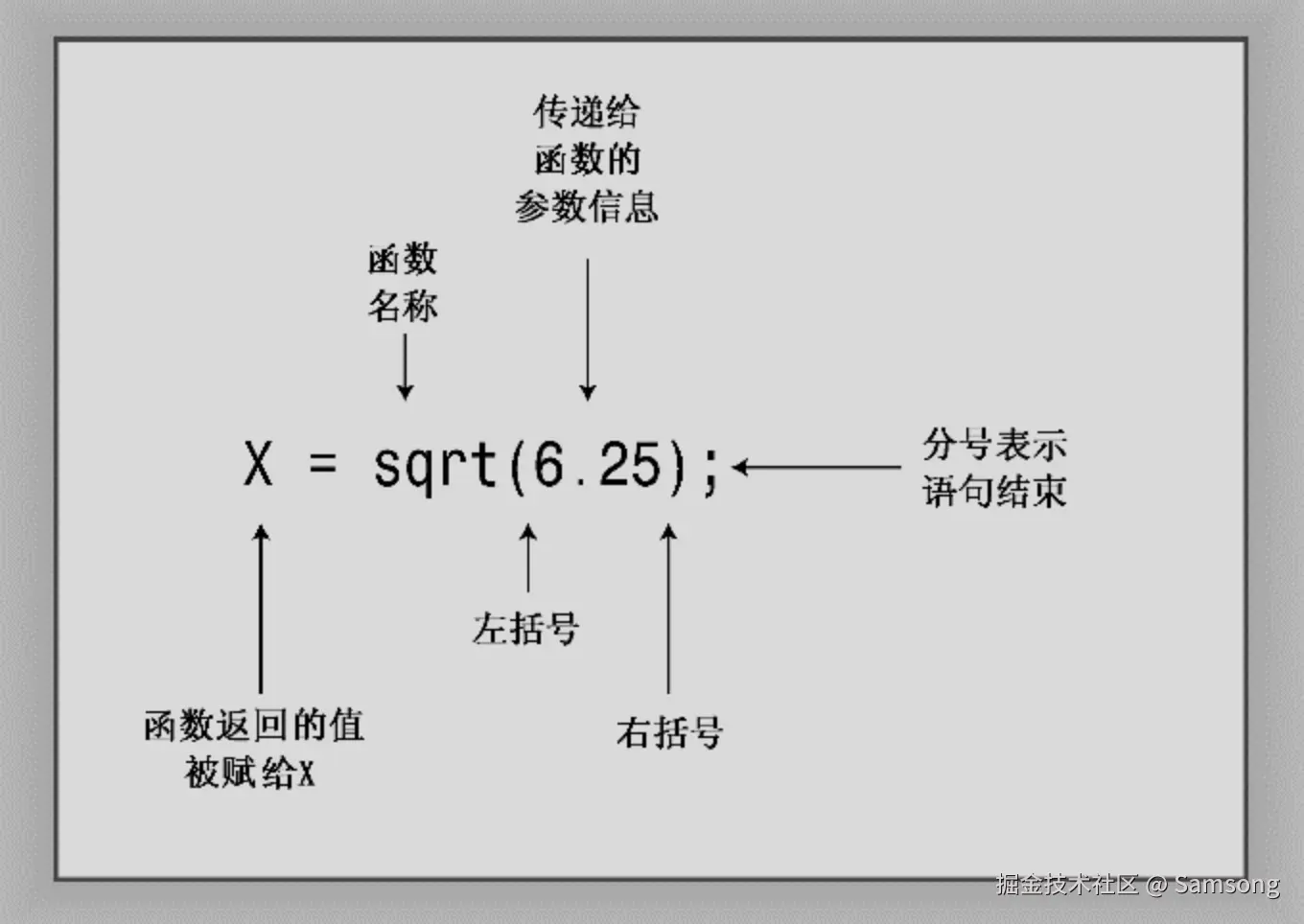
C++函数可被其他函数激活或调用,函数头描述了函数与调用它的函数之间的接口。位于函数名前面的部分叫做函数返回类型,它描述的是从函数返回给调用它的函数的信息。函数名后括号中的部分叫做形参列表(argument list)或参数列表(parameter list);它描述的是从调用函数传递给被调用的函数的信息。
通常,main( )被启动代码调用,而启动代码是由编译器添加到程序中的,是程序和操作系统(UNIX、Windows 7或其他操作系统)之间的桥梁。事实上,该函数头描述的是main( )和操作系统之间的接口。
如果编译器到达main( )函数末尾时没有遇到返回语句,则认为main( )函数以如下语句结尾:
return 0
这条隐含的返回语句只适用于main( )函数,而不适用于其他函数。
#include <iostream> 该编译指令导致预处理器将iostream文件的内容添加到程序中。#include 。原始文件没有被修改,而是将源代码文件和iostream组合成一个复合文件,编译的下一阶段将使用该文件。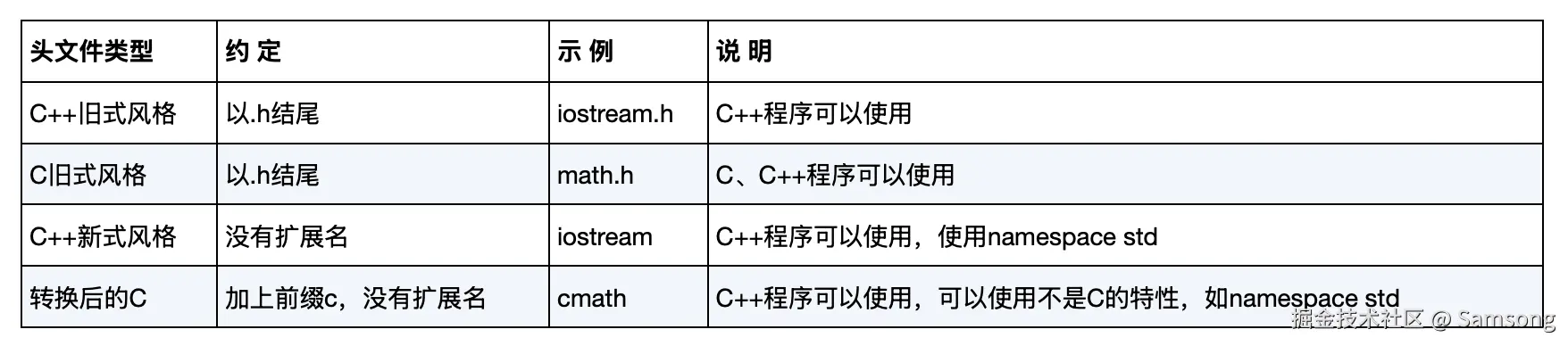
using namespace std; 这个using编译指令使得std名称空间中的所有名称都可用。using std::cout。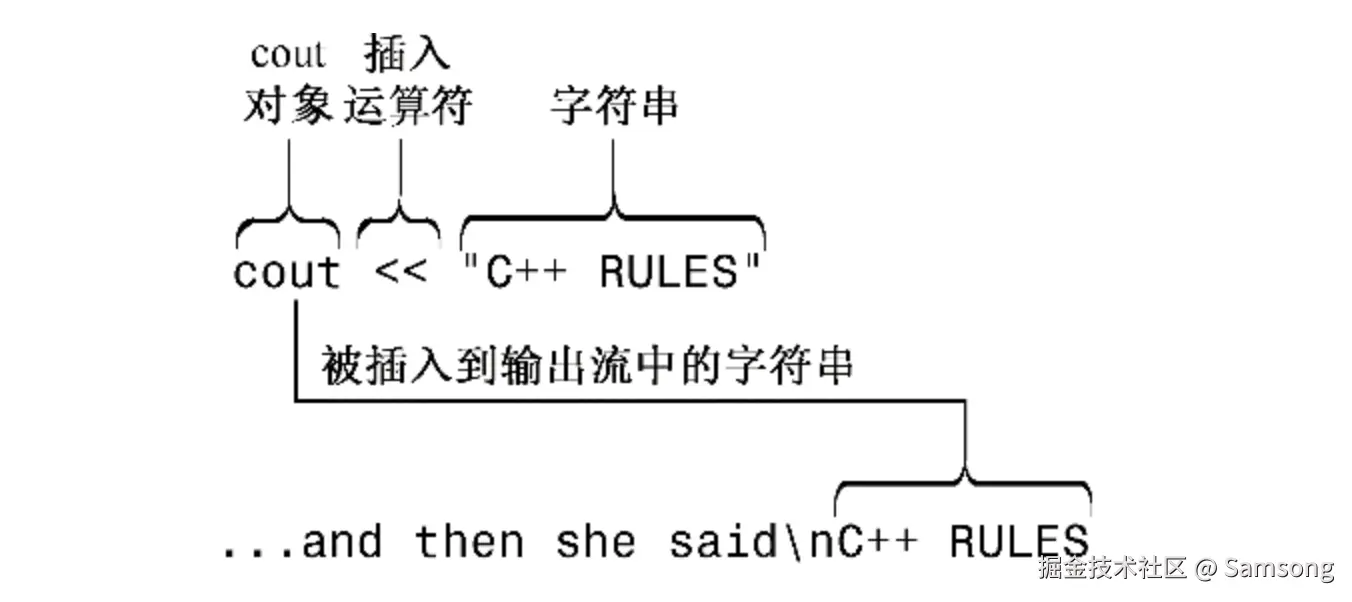
// carrots.cpp -- food processing program
// uses and displays a variable
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
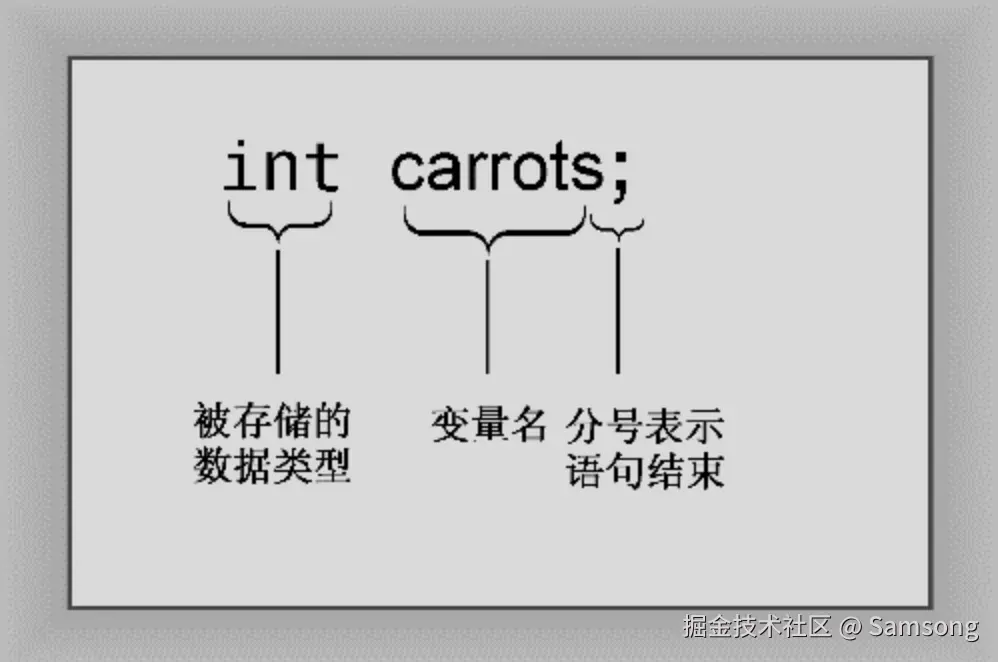
int carrots; // declare an integer variable
carrots = 25; // assign a value to the variable
cout << "I have ";
cout << carrots; // display the value of the variable
cout << " carrots.";
cout << endl;
carrots = carrots - 1; // modify the variable
cout << "Crunch, crunch. Now I have " << carrots << " carrots." << endl;
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
// getinfo.cpp -- input and output
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int carrots;
cout << "How many carrots do you have?" << endl;
cin >> carrots; // C++ input
cout << "Here are two more. ";
carrots = carrots + 2;
// the next line concatenates output
cout << "Now you have " << carrots << " carrots." << endl;
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
cout << "Now you have " << carrots << " carrots." << endl;
// sqrt.cpp -- using the sqrt() function
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath> // or math.h
int main()
{
using namespace std;
double area;
cout << "Enter the floor area, in square feet, of your home: ";
cin >> area;
double side;
side = sqrt(area);
cout << "That's the equivalent of a square " << side
<< " feet to the side." << endl;
cout << "How fascinating!" << endl;
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
double sqrt(double);double pow(double, double);。int rand(void);。void bucks(double);。// ourfunc.cpp -- defining your own function
#include <iostream>
void simon(int); // function prototype for simon()
int main()
{
using namespace std;
simon(3); // call the simon() function
cout << "Pick an integer: ";
int count;
cin >> count;
simon(count); // call it again
cout << "Done!" << endl;
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
void simon(int n) // define the simon() function
{
using namespace std;
cout << "Simon says touch your toes " << n << " times." << endl;
} // void functions don't need return statements

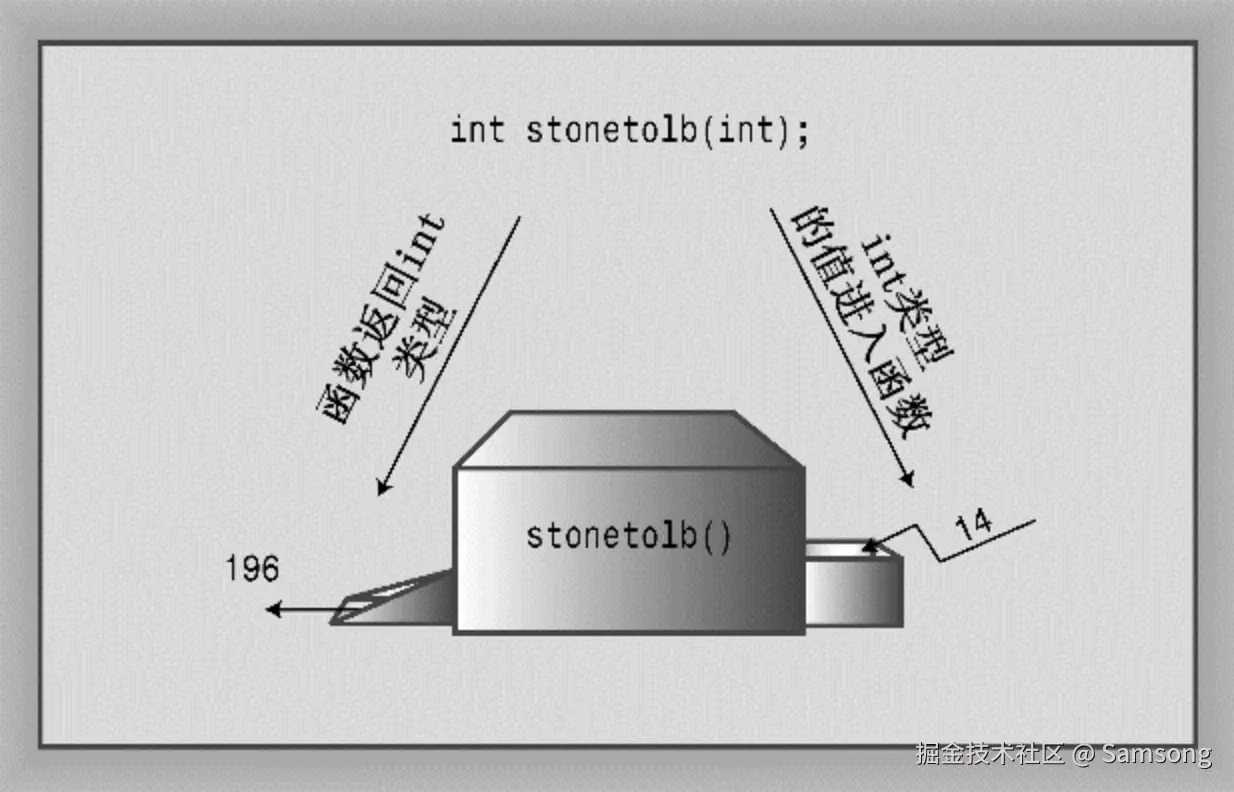
// convert.cpp -- converts stone to pounds
#include <iostream>
int stonetolb(int); // function prototype
int main()
{
using namespace std;
int stone;
cout << "Enter the weight in stone: ";
cin >> stone;
int pounds = stonetolb(stone);
cout << stone << " stone = ";
cout << pounds << " pounds." << endl;
// cin.get();
// cin.get();
return 0;
}
int stonetolb(int sts)
{
return 14 * sts;
}
当前通行的理念是,只让需要访问名称空间std的函数访问它是更好的选择。 让程序能够访问名称空间std的方法有多种:
具体代码详见《C++ Primer Plus(第6版)》编程练习源代码