强者的自我修养免安装绿色中文版
4.29G · 2025-11-02
mybatis是一个持久层的框架,是apache下的顶级项目。
mybatis托管到goolecode下,再后来托管到github下(https://gi*t*h*ub.com/mybatis/mybatis-3/releases)。
mybatis让程序将主要精力放在sql上,通过mybatis提供的映射方式,自由灵活生成(半自动化,大部分需要程序员编写sql)满足需要sql语句。
mybatis可以将向 preparedStatement中的输入参数自动进行输入映射,将查询结果集灵活映射成java对象。(输出映射)
支持普通SQL查询,存储过程和高级映射
|
序号 |
Mybatis |
hibernate |
|
1. |
iBatis SSI 2002年诞生 Cliton begin |
2001年 Given King |
|
2. |
2010年5月由apache投奔google |
Jboss,apache |
|
3. |
基于SQL 面向结果集 |
基于面向对象 HQL |
|
4. |
效率高 |
效率低 |
|
5. |
SqlSessionFactory |
SessionFactory |
|
6. |
SqlSession |
Session |
|
7. |
sqlMapConfig.xml |
Hibernate.cfg.xml |
|
8. |
userMapper.xml |
映射文件 user.hbm.xml |
Hibernate面向对象,它使用HQL,可以无需写SQL语句。全自动ORM。
Mybatis面向对象,它使用SQL语句,很依赖于SQL语句。半自动ORM。
hibernate:是一个标准ORM框架(对象关系映射)。入门门槛较高的,不需要程序写sql,sql语句自动生成了。
对sql语句进行优化、修改比较困难的。
应用场景:
适用与需求变化不多的中小型项目,比如:后台管理系统,erp、orm、oa。。
mybatis:专注是sql本身,需要程序员自己编写sql语句,sql修改、优化比较方便。mybatis是一个不完全 的ORM框架,虽然程序员自己写sql,mybatis 也可以实现映射(输入映射、输出映射)。
应用场景:
适用与需求变化较多的项目,比如:互联网项目。
企业进行技术选型,以低成本 高回报作为技术选型的原则,根据项目组的技术力量进行选择。
|
SqlMapConfig.xml(是mybatis的全局配置文件,名称不固定的) 配置了数据源、事务等mybatis运行环境 配置映射文件(配置sql语句) mapper.xml(映射文件)、mapper.xml、mapper.xml..... |
===>>
|
SqlSessionFactory(会话工厂),根据配置文件创建工厂 作用:创建SqlSession |
===>>
|
SqlSession(会话),是一个接口,面向用户(程序员)的接口 作用:操作数据库(发出sql增、删、改、查) |
===>
|
Executor(执行器),是一个接口(基本执行器、缓存执行器) 作用:SqlSession内部通过执行器操作数据库 |
==>
|
mapped statement(底层封装对象) 作用:对操作数据库存储封装,包括 sql语句,输入参数、输出结果类型 |
===>> mysql
mybatis是一人持久层框架,mybatis是一个不完全的ORM框架。sql语句需要程序员自己去编写,但是mybatis也有映射(输入参数映射、输出结果映射)。
mybatis入门门槛不高,学习成本低,让程序员把精力放在sql语句上,对sql语句优化非常方便,适用与需求变化较多项目,比如互联网项目。
1、配置mybatis的配置文件,SqlMapConfig.xml(名称不固定)
2、通过配置文件,加载mybatis运行环境,创建SqlSessionFactory会话工厂
SqlSessionFactory在实际使用时按单例方式。
3、通过SqlSessionFactory创建SqlSession
SqlSession是一个面向用户接口(提供操作数据库方法),实现对象是线程不安全的,建议sqlSession应用场合在方法体内。
4、调用sqlSession的方法去操作数据。
如果需要提交事务,需要执行SqlSession的commit()方法。
5、释放资源,关闭SqlSession
1、原始dao 的方法
需要程序员编写dao接口和实现类
需要在dao实现类中注入一个SqlSessionFactory工厂。
2、mapper代理开发方法(建议使用)
只需要程序员编写mapper接口(就是dao接口)
程序员在编写mapper.xml(映射文件)和mapper.java需要遵循一个开发规范:
1、mapper.xml中namespace就是mapper.java的类全路径。
2、mapper.xml中statement的id和mapper.java中方法名一致。
3、mapper.xml中statement的parameterType指定输入参数的类型和mapper.java的方法输入 参数类型一致。
4、mapper.xml中statement的resultType指定输出结果的类型和mapper.java的方法返回值类型一致。
SqlMapConfig.xml是Mybatis的全局配置文件,它的名称可以是任意,但是一般命名都为(SqlMapConfig)
配置mybatis的运行环境,数据源、事务等。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://myba*t*is.or*g/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
<!-- 配置mybatis的环境信息,和spring整合后不在使用environments配置数据库 -->
<environments default="developments">
<environment id="developments">
<!-- 配置JDBC事务控制,由mybatis进行管理 -->
<transactionManager type="JDBC"></transactionManager>
<!-- 配置数据源,采用mybatis连接池 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="12345678"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<!-- 加载映射文件 -->
<mappers>
<mapper resource="User.xml"/>
<mapper resource="Teacher.xml"/>
</mappers>
</configuration>
properties(属性)
settings(全局配置参数)
typeAliases(类型别名)
typeHandlers(类型处理器)
objectFactory(对象工厂)
plugins(插件)
environments(环境集合属性对象)
environment(环境子属性对象)
transactionManager(事务管理)
dataSource(数据源)
mappers(映射器)
需求:
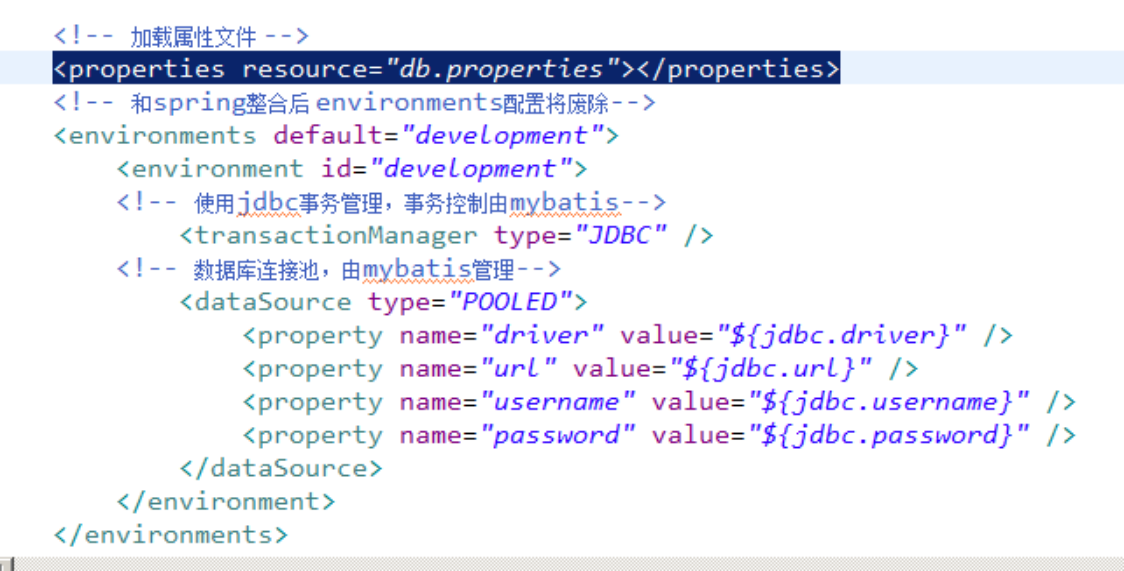
将数据库连接参数单独配置在db.properties中,只需要在SqlMapConfig.xml中加载db.properties的属性值。
在SqlMapConfig.xml中就不需要对数据库连接参数硬编码。
将数据库连接参数只配置在db.properties中,原因:方便对参数进行统一管理,其它xml可以引用该db.properties。
在sqlMapConfig.xml加载属性文件:
properties特性:
注意: MyBatis 将按照下面的顺序来加载属性:
建议:
不要在properties元素体内添加任何属性值,只将属性值定义在properties文件中。
在properties文件中定义属性名要有一定的特殊性,如:XXXXX.XXXXX.XXXX
我们说过数据库的连接信息一般要放到一个额外的.properties文件中,mybatis允许我们这样做。
首先,修改sqlMapConfig.xml文件:
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driverClass}"/>
<property name="url" value="${url}"/>
<property name="username" value="${username}"/>
<property name="password" value="${password}"/>
</dataSource>联想spring的dataSource配置方式,不难理解。
占位符的数据来源配置有三种方式:
第一种使用方式:在SqlSessionFactoryBuilder的build方法中,还提供了额外传入Properties对象的方法:
public SqlSessionFactory build(InputStream inputStream, Properties properties)
这个方法后面的Properties对象就可以做为sqlMapConfig.xml中的参数来源。所以,我们可以这样来使用:
Properties p=new Properties();
p.load(Resources.getResourceAsStream("db.properties"));
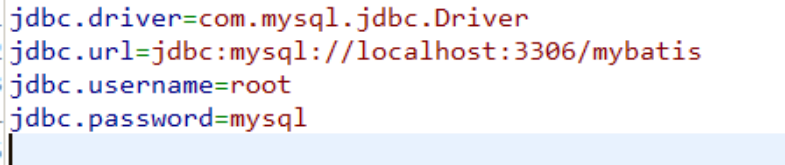
并在classpath下定义一个db.properties文件:
driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisdb?characterEncoding=utf-8
username=root
password=root第二种使用方式:在mybatis-config.xml中有properties这样一个标签,那么我们可以在mybatis-config.xml中定义:
<properties>
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///mybatisdb?characterEncoding=utf-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</properties>第三种方式:在mybatis-config.xml中的properties元素中,引入外部的properties文件:
<properties resource="db.properties" />
并在classpath中添加db.properties文件即可。
第三种方式和第二种方式可以混用,即:
db.properties文件中:
driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatisdb?characterEncoding=utf-8
sqlMapConfig.xml文件中:
<properties resource="db.properties">
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</properties>
三者的优先级为:
代码传入的Properties > resource加载的Properties > properties元素中定义的property。
mybatis框架在运行时可以调整一些运行参数。
比如:开启二级缓存、开启延迟加载。。
全局参数将会影响mybatis的运行行为。
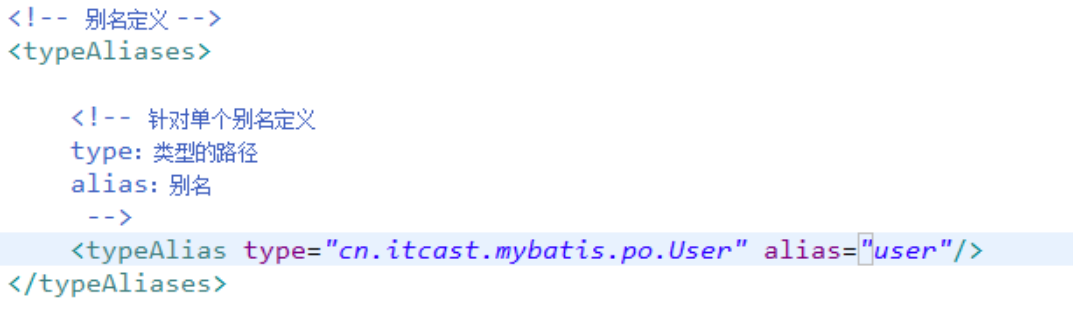
在mapper.xml中,定义很多的statement,statement需要parameterType指定输入参数的类型、需要resultType指定输出结果的映射类型。
如果在指定类型时输入类型全路径,不方便进行开发,可以针对parameterType或resultType指定的类型定义一些别名,在mapper.xml中通过别名定义,方便开发。
|
别名 |
映射的类型 |
|
_byte |
byte |
|
_long |
long |
|
_short |
short |
|
_int |
int |
|
_integer |
int |
|
_double |
double |
|
_float |
float |
|
_boolean |
boolean |
|
string |
String |
|
byte |
Byte |
|
long |
Long |
|
short |
Short |
|
int |
Integer |
|
integer |
Integer |
|
double |
Double |
|
float |
Float |
|
boolean |
Boolean |
|
date |
Date |
|
decimal |
BigDecimal |
|
bigdecimal |
BigDecimal |
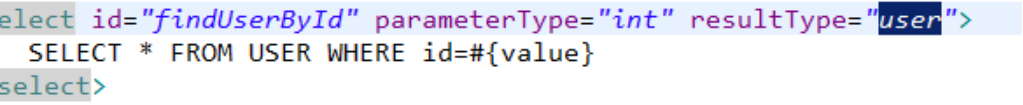
引用别名:
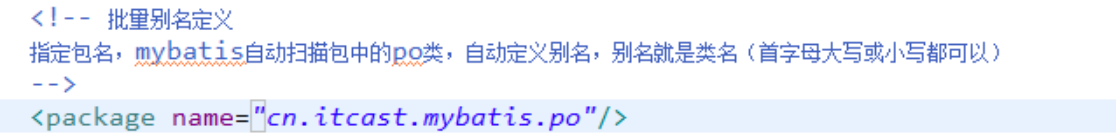
mybatis中通过typeHandlers完成jdbc类型和java类型的转换。
通常情况下,mybatis提供的类型处理器满足日常需要,不需要自定义.
mybatis支持类型处理器:
|
类型处理器 |
Java类型 |
JDBC类型 |
|
BooleanTypeHandler |
Boolean,boolean |
任何兼容的布尔值 |
|
ByteTypeHandler |
Byte,byte |
任何兼容的数字或字节类型 |
|
ShortTypeHandler |
Short,short |
任何兼容的数字或短整型 |
|
IntegerTypeHandler |
Integer,int |
任何兼容的数字和整型 |
|
LongTypeHandler |
Long,long |
任何兼容的数字或长整型 |
|
FloatTypeHandler |
Float,float |
任何兼容的数字或单精度浮点型 |
|
DoubleTypeHandler |
Double,double |
任何兼容的数字或双精度浮点型 |
|
BigDecimalTypeHandler |
BigDecimal |
任何兼容的数字或十进制小数类型 |
|
StringTypeHandler |
String |
CHAR和VARCHAR类型 |
|
ClobTypeHandler |
String |
CLOB和LONGVARCHAR类型 |
|
NStringTypeHandler |
String |
NVARCHAR和NCHAR类型 |
|
NClobTypeHandler |
String |
NCLOB类型 |
|
ByteArrayTypeHandler |
byte[] |
任何兼容的字节流类型 |
|
BlobTypeHandler |
byte[] |
BLOB和LONGVARBINARY类型 |
|
DateTypeHandler |
Date(java.util) |
TIMESTAMP类型 |
|
DateOnlyTypeHandler |
Date(java.util) |
DATE类型 |
|
TimeOnlyTypeHandler |
Date(java.util) |
TIME类型 |
|
SqlTimestampTypeHandler |
Timestamp(java.sql) |
TIMESTAMP类型 |
|
SqlDateTypeHandler |
Date(java.sql) |
DATE类型 |
|
SqlTimeTypeHandler |
Time(java.sql) |
TIME类型 |
|
ObjectTypeHandler |
任意 |
其他或未指定类型 |
|
EnumTypeHandler |
Enumeration类型 |
VARCHAR-任何兼容的字符串类型,作为代码存储(而不是索引)。 |
Mapper:代表这是一个对象的映射关系
namespace:为当前映射关系创建的命名空间,要引用这个映射关系里面定义的东西,需要带上这个命名空间。还有其他非常重要的作用,之后会看到。namespace等于mapper接口地址
insert:代表定义了一个插入操作(即SQL的insert操作)
id:为这个插入操作起一个名字,以后要保存user这个对象,其实就是要调用这个插入操作。
keyProperty:代表主键对应对象的属性名称。有点像hibernate里面那个id元素。
parameterType:mybatis里面非常重要的一个元素,代表这个insert操作对应的方法需要传入一个什么类型的对象。
useGeneratedKeys:代表告诉mybatis,使用autoGeneratedKey来获取数据库帮我们自动生成的ID。(这个方法在jdbc中讲过)
l标签 select/insert/update/delete
nSQL语句,不区分大小写,它使用的默认使用PrepareStatement,预编译,防止SQL注入。
文件名可以随意命名,习惯使用 PO对象名+Mapper.xml



mapper.java接口中的方法名和mapper.xml中statement的id一致
mapper.java接口中的方法输入参数类型和mapper.xml中statement的parameterType指定的类型一致。
mapper.java接口中的方法返回值类型和mapper.xml中statement的resultType指定的类型一致。
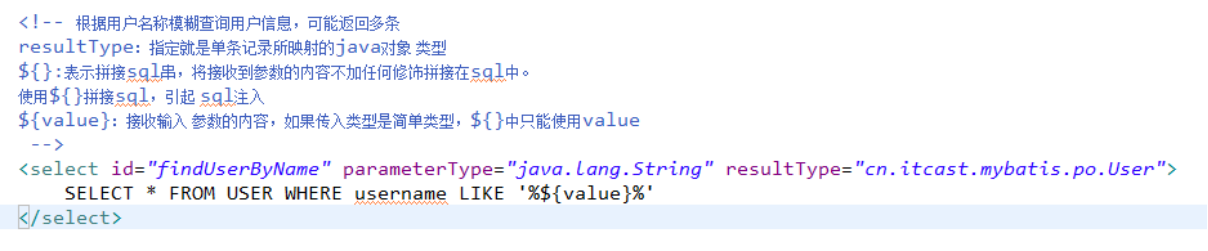
模糊查询:
使用User.xml,添加根据用户名称模糊查询用户信息的sql语句。
<if test="record.activityName != null and record.activityName != ''">
and activity_name like '${record.activityName}%'
</if>用这样的$是进行字符串拼接的存在注入的风险
例如字符串:%' and bigdescription like '阳城
解决方法:
bind + #{} 模糊查询 防止SQL注入 (#{}进行预编译,传递的参数不进行编译,只作为参数,相当于PreparedStatement)
<select id="selectBlogsLike" resultType="Blog">
<bind name="pattern" value="'%' + _parameter.getTitle() + '%'" />
SELECT * FROM BLOG
WHERE title LIKE #{pattern}
</select>
<if test="userName != null and userName != '' ">
<!-- and user_name like concat('%',#{userName},'%') -->
<bind name="userNameLike" value=" '%' + userName + '%' "/>
and user_name like #{userNameLike}
</if>
当传入的只有一个参数时_parameter就可以获取到值
<select id="findShopByName" parameterType="java.lang.String" resultType="com.dongao.project.statistics.overall.domain.ShopVo">
<bind name="shopNameLike" value="'%' + _parameter + '%'" />
<!-- 根据店铺名查询店铺信息 -->
select id,shop_name as name from ec_shop where shop_name like #{shopNameLike}
</select>另一种方法是使用函数
like concat('%',#{userName},'%')
使用concat函数连接字符串,在MySQL中,这个函数支持多个参数,但是在Oracle中只支持两个参数。 由于不同数据库之间的语法差异,如果更换了数据库,有些SQL语句可能就需要重写
在 User.xml中配置添加用户的Statement
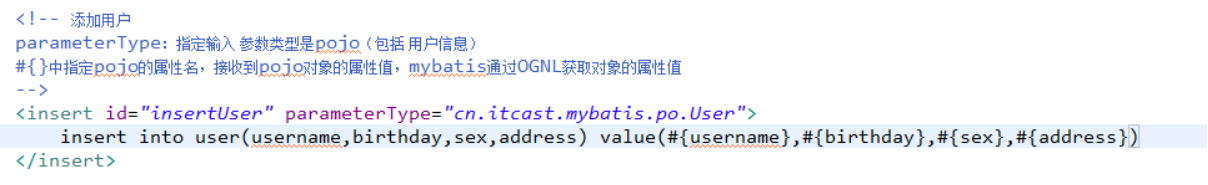
其属性如下:
parameterType ,入参的全限定类名或类型别名
keyColumn ,设置数据表自动生成的主键名。对特定数据库(如PostgreSQL),若自动生成的主键不是第一个字段则必须设置
keyProperty ,默认值unset,用于设置getGeneratedKeys方法或selectKey子元素返回值将赋值到领域模型的哪个属性中
useGeneratedKeys ,取值范围true|false(默认值),设置是否使用JDBC的getGenereatedKeys方法获取主键并赋值到keyProperty设置的领域模型属性中。MySQL和SQLServer执行auto-generated key field,因此当数据库设置好自增长主键后,可通过JDBC的getGeneratedKeys方法获取。但像Oralce等不支持auto-generated key field的数据库就不能用这种方法获取主键了
statementType ,取值范围STATEMENT,PREPARED(默认值),CALLABLE
flushCache ,取值范围true(默认值)|false,设置执行该操作后是否会清空二级缓存和本地缓存
timeout ,默认为unset(依赖jdbc驱动器的设置),设置执行该操作的最大时限,超时将抛异常
databaseId ,取值范围oracle|mysql等,表示数据库厂家,元素内部可通过`<if test="_databaseId = 'oracle'">`来为特定数据库指定不同的sql语句
一般的INSERT操作——返回值为插入的记录数目
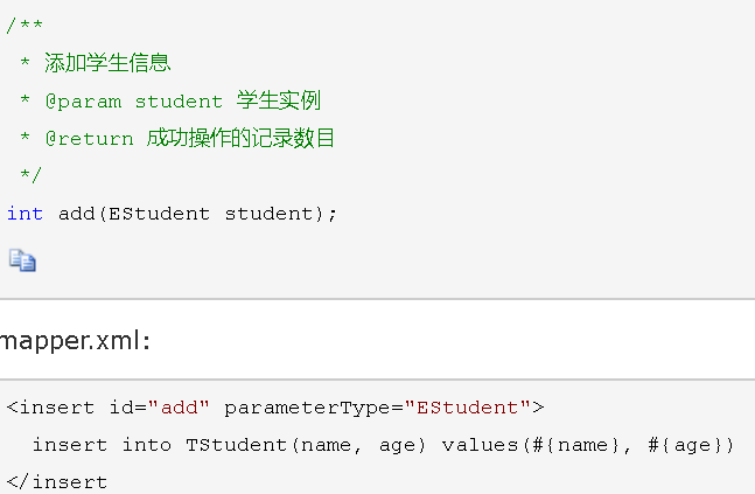
方法一:
mysql自增主键,执行insert提交之前自动生成一个自增主键。
通过mysql函数获取到刚插入记录的自增主键:
LAST_INSERT_ID()
是insert之后调用此函数。
修改insertUser定义:
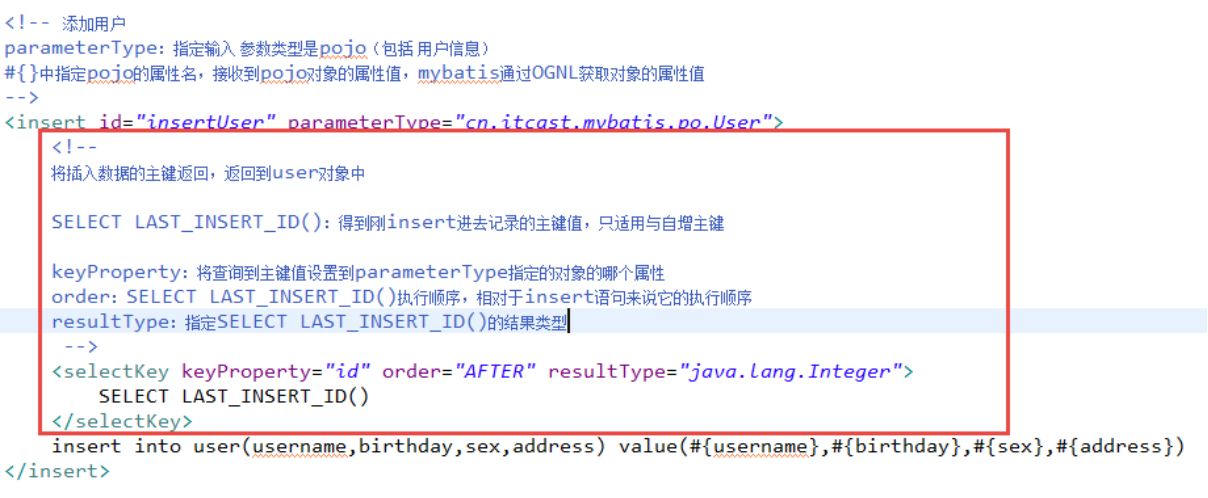
LAST_INSERT_ID()
方法二:
<insert id="insert" keyColumn="id" keyProperty="id" parameterType="com.dongao.marketing.pojo.MpShareFissionPo" useGeneratedKeys="true">
insert into mp_share_fission (parent_id, activity_id, activity_code,activity_name, open_id, union_id,nick_name, head_url, create_time
)
values (#{parentId,jdbcType=BIGINT}, #{activityId,jdbcType=BIGINT}, #{activityCode,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{activityName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{openId,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{unionId,jdbcType=VARCHAR},
#{nickName,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{headUrl,jdbcType=VARCHAR}, #{createTime,jdbcType=TIMESTAMP}
)
</insert>指定自动增长useGeneratedKeys回收主键的字段keyProperty,这样插入以后的pojo这里的MpShareFissionPo对象中就有了主键的值了
使用mysql的uuid()函数生成主键,需要修改表中id字段类型为string,长度设置成35位。
执行思路:
先通过uuid()查询到主键,将主键输入 到sql语句中。
执行uuid()语句顺序相对于insert语句之前执行。
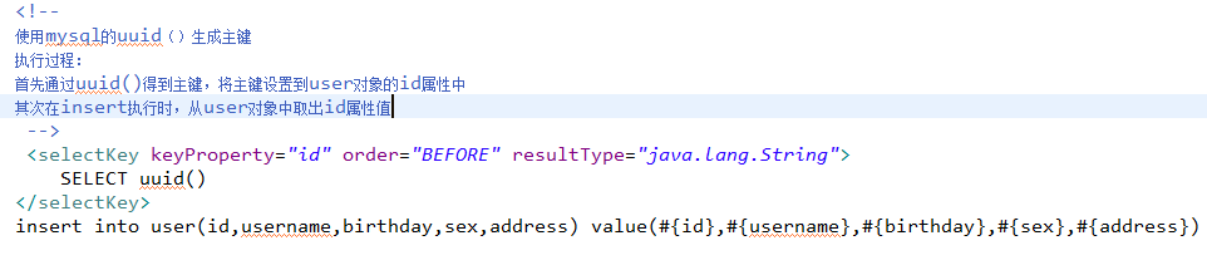
通过oracle的序列生成主键:
<selectKey keyProperty="id" order="BEFORE" resultType="java.lang.String">
SELECT 序列名.nextval()
</selectKey>
insert into user(id,username,birthday,sex,address) value(#{id},#{username},#{birthday},#{sex},#{address})
在映射文件中通过parameterType指定输入 参数的类型。
在映射文件中通过resultType指定输出结果的类型。
#{}表示一个占位符号,#{}接收输入参数,类型可以是简单类型,pojo、hashmap。
如果接收简单类型,#{}中可以写成value或其它名称。
#{}接收pojo对象值,通过OGNL读取对象中的属性值,通过属性.属性.属性...的方式获取对象属性值。
${}表示一个拼接符号,会引用sql注入,所以不建议使用${}。
${}接收输入参数,类型可以是简单类型,pojo、hashmap。
如果接收简单类型,${}中只能写成value。
${}接收pojo对象值,通过OGNL读取对象中的属性值,通过属性.属性.属性...的方式获取对象属性值。
在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置映射文件位置

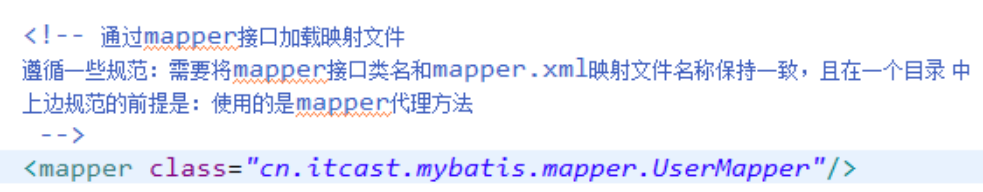
按照上边的规范,将mapper.java和mapper.xml放在一个目录 ,且同名。

也可以在sqlSessionFactory指定
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:spring/sqlMapConfig.xml"/>
<property name="mapperLocations">
<value>classpath:mybatis/*.xml</value>
</property>
</bean>参数:parameterMap 废弃,它为了兼容前期的项目;parameterType 它支持很丰富的类型 int/integer/string/double/list/map/实体
parameterType可以不写,mabatis会自动识别
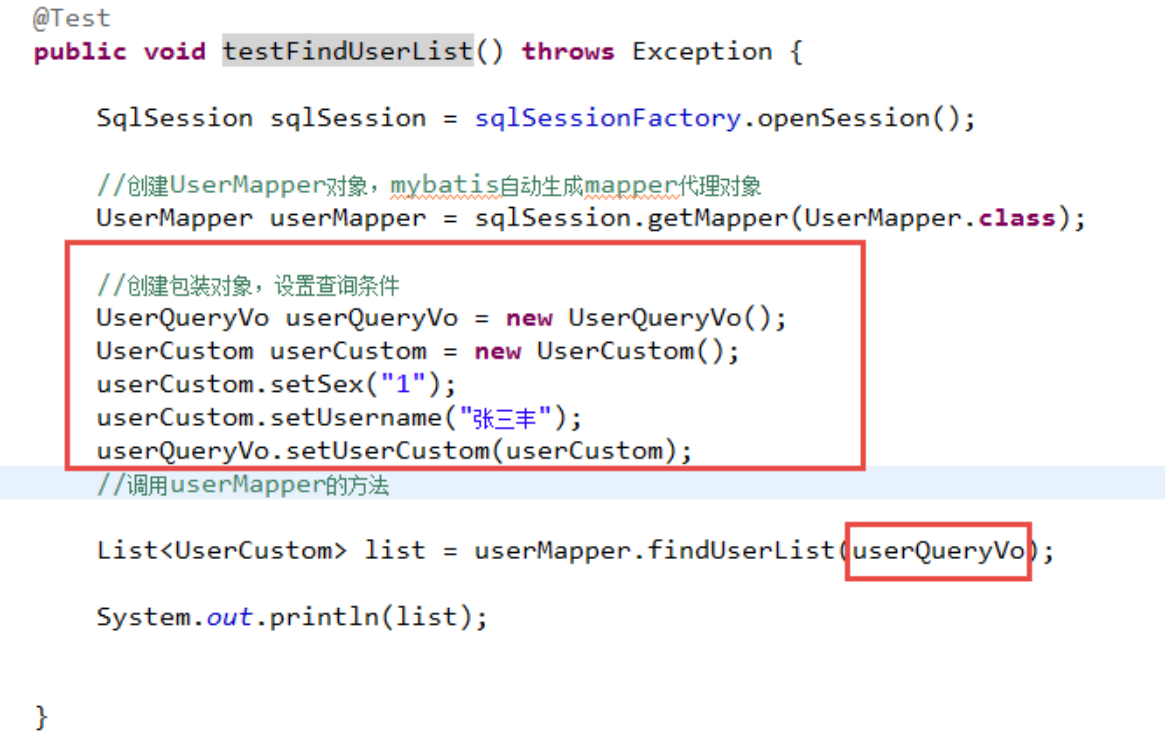
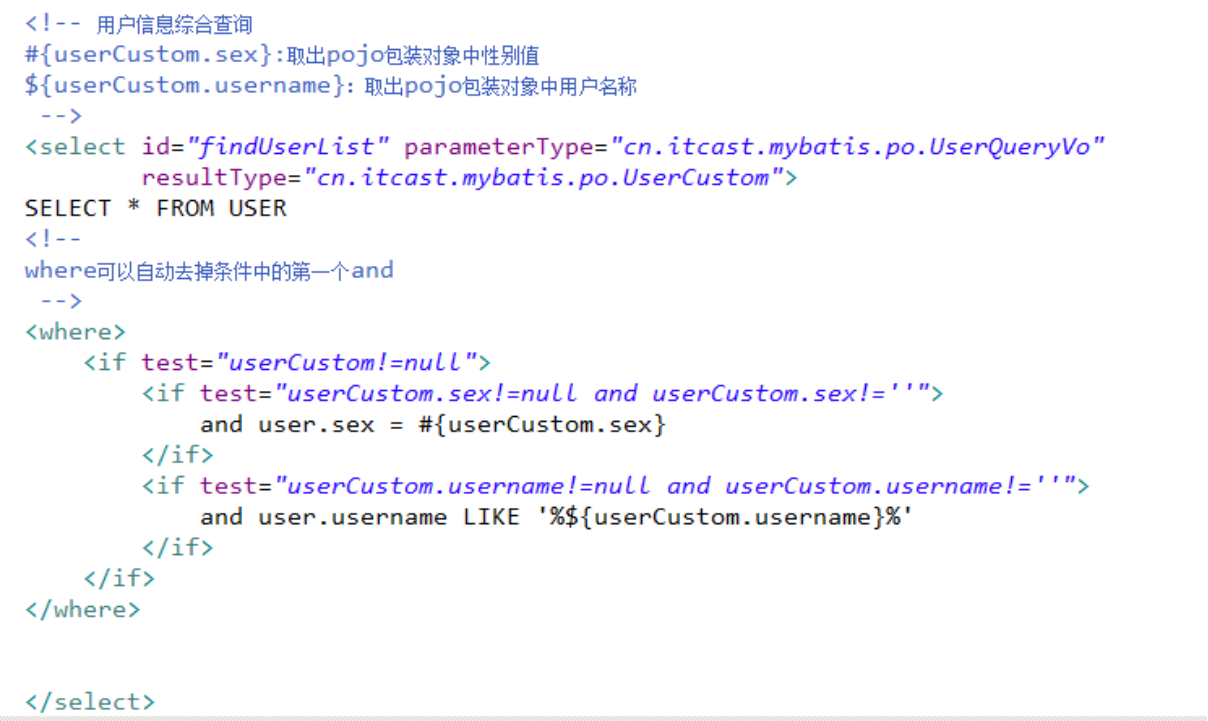
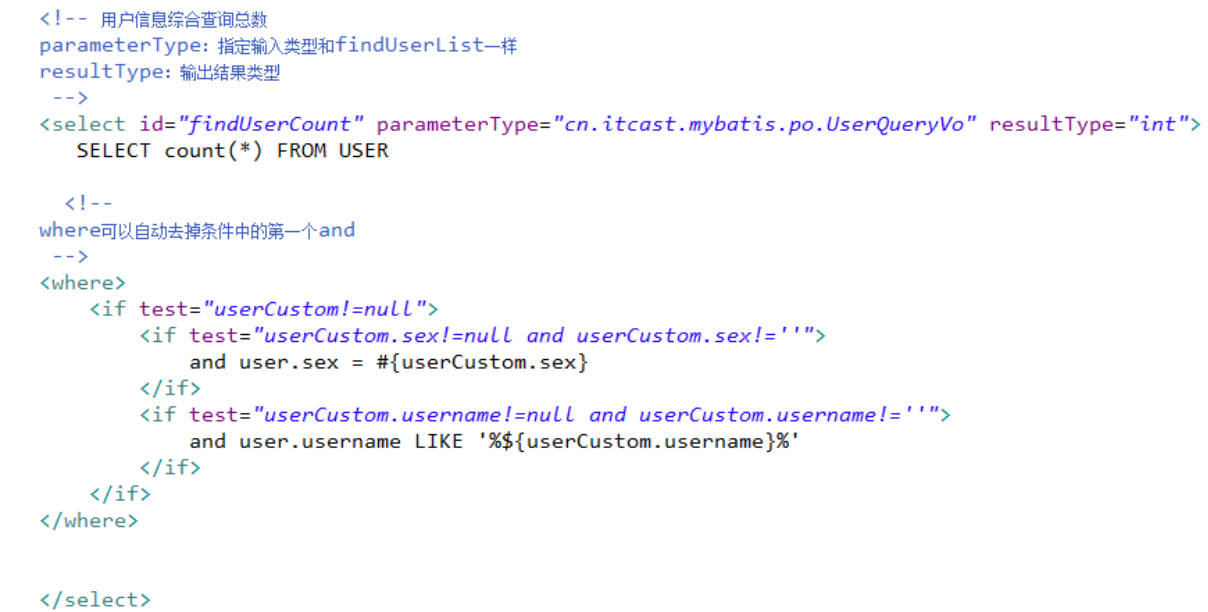
完成用户信息的综合查询,需要传入查询条件很复杂(可能包括用户信息、其它信息,比如商品、订单的)
针对上边需求,建议使用自定义的包装类型的pojo。
在包装类型的pojo中将复杂的查询条件包装进去。
在UserMapper.xml中定义用户信息综合查询(查询条件复杂,通过高级查询进行复杂关联查询)。
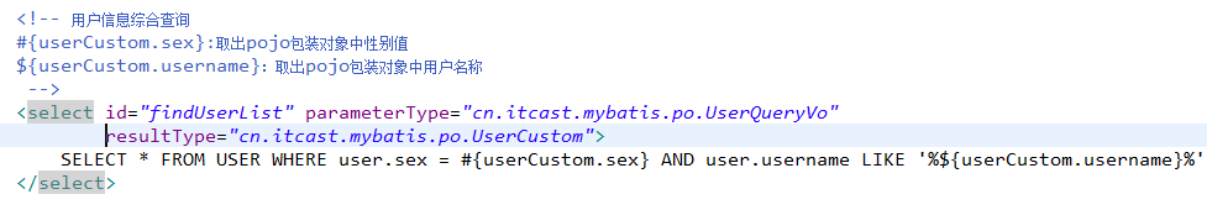

使用resultType进行输出映射,只有查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性名一致,该列才可以映射成功。
如果查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性名全部不一致,没有创建pojo对象。
只要查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性有一个一致,就会创建pojo对象。
String getEmpNameById(Integer id);
<select id="getEmpNameById" resultType="string">
select username from t_employee where id = #{id}
</select>查询的列名与pojo属性名一致
Employee getEmpById(Integer id);
<select id="getEmpById" resultType="employee">
select * from t_employee where id = #{id}
</select>
List<Employee> getAllEmps();
<!--注意这里的 resultType 返回值类型是集合内存储数据的类型,不是 'list'-->
<select id="getAllEmps" resultType="employee">
select * from t_employee
</select>如果查询的结果是一条,我们可以把查询的数据以{表字段名, 对应的值}方式存入到Map中。
Map<String, Object> getEmpAsMapById(Integer id);
<!--注意这里的 resultType 返回值类型是 'map'-->
<select id="getEmpAsMapById" resultType="map">
select * from t_employee where id = #{id}
</select>
// 查询所有员工的信息,把数据库中的 'id' 字段作为 key,对应的 value 封装成 Employee 对象
// @MapKey 中的值表示用数据库中的哪个字段名作 key
@MapKey("id")
Map<Integer, Employee> getAllEmpsAsMap();
<!--注意 resultType 返回值类型,不再是 'map',而是 Map 的 value 对应的 JavaBean 类型-->
<select id="getAllEmpsAsMap" resultType="employee">
select * from t_employee
</select>
不管是输出的pojo单个对象还是一个列表(list中包括pojo),在mapper.xml中resultType指定的类型是一样的。
在mapper.java指定的方法返回值类型不一样:
1、输出单个pojo对象,方法返回值是单个对象类型
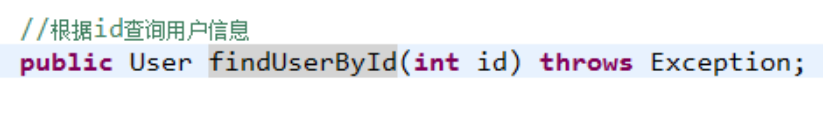
2、输出pojo对象list,方法返回值是List<Pojo>

生成的动态代理对象中是根据mapper方法的返回值类型确定是调用selectOne(返回单个对象调用)还是selectList (返回集合对象调用 ).
mybatis中使用resultMap完成高级输出结果映射。
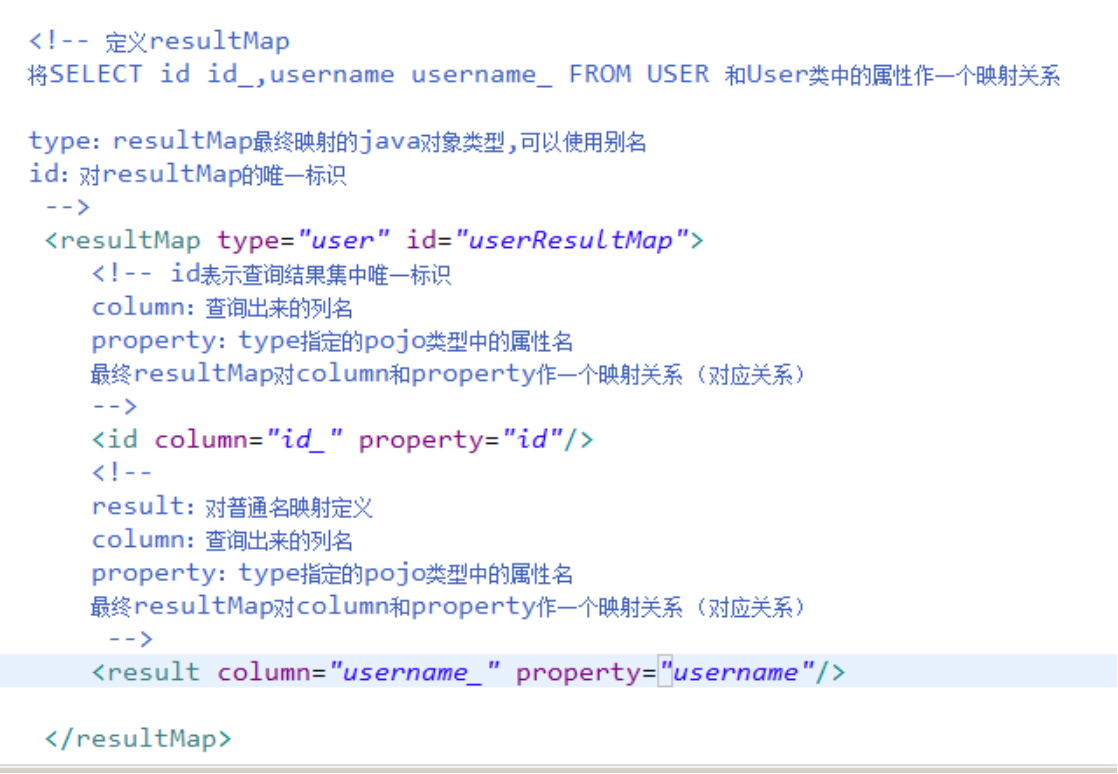
如果查询出来的列名和pojo的属性名不一致,通过定义一个resultMap对列名和pojo属性名之间作一个映射关系。
1、定义resultMap
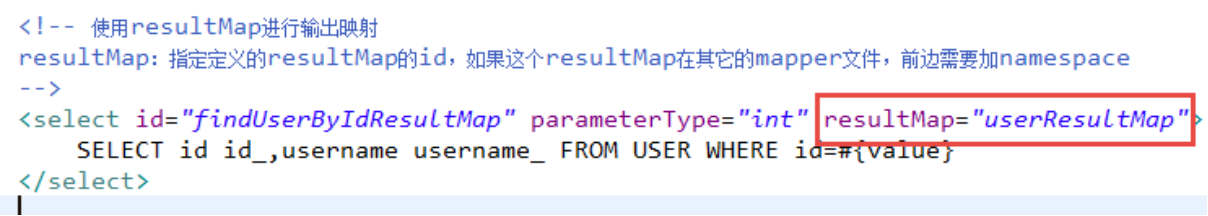
2、使用resultMap作为statement的输出映射类型
SELECT id id_,username username_ FROM USER WHERE id=#{value}
User类中属性名和上边查询列名不一致。
resultMap定义了一个ORM的具体映射方式。
1,type:代表O,即最终返回的对象类型
2,id:为该映射设置一个名称,这个名称就是在get或list中使用的resultMap对应的id
3,id/result:对应这属性的映射,可以参考hibernate的property。id和result的区别在于,id一般用于映射主键,可以提高速度,result一般对于普通的属性。
设置完成后,就可以将对象正常get了。

使用resultType进行输出映射,只有查询出来的列名和pojo中的属性名一致,该列才可以映射成功。
如果查询出来的列名和pojo的属性名不一致,通过定义一个resultMap对列名和pojo属性名之间作一个映射关系。
mybatis核心 对sql语句进行灵活操作,通过表达式进行判断,对sql进行灵活拼接、组装。
<where> 自动去除第一个条件的 and 或者 or
<set> 自动去除SQL语句中最后一个的逗号
<!-- 带条件的动态SQL -->
<select id="find" parameterType="cn.itcast.ssm.domain.User" resultMap="userRM">
select * from user
<where>
<if test="userName!=null">
and user_name like #{userName}
</if>
<if test="age!=null">
and age>#{age}
</if>
</where>
</select>
<update id="update" parameterType="cn.itcast.ssm.domain.User">
update user
<set>
<if test="userName!=null">
user_name=#{userName},
</if>
<if test="age!=null">
age=#{age},
</if>
</set>
where id=#{id}
</update>
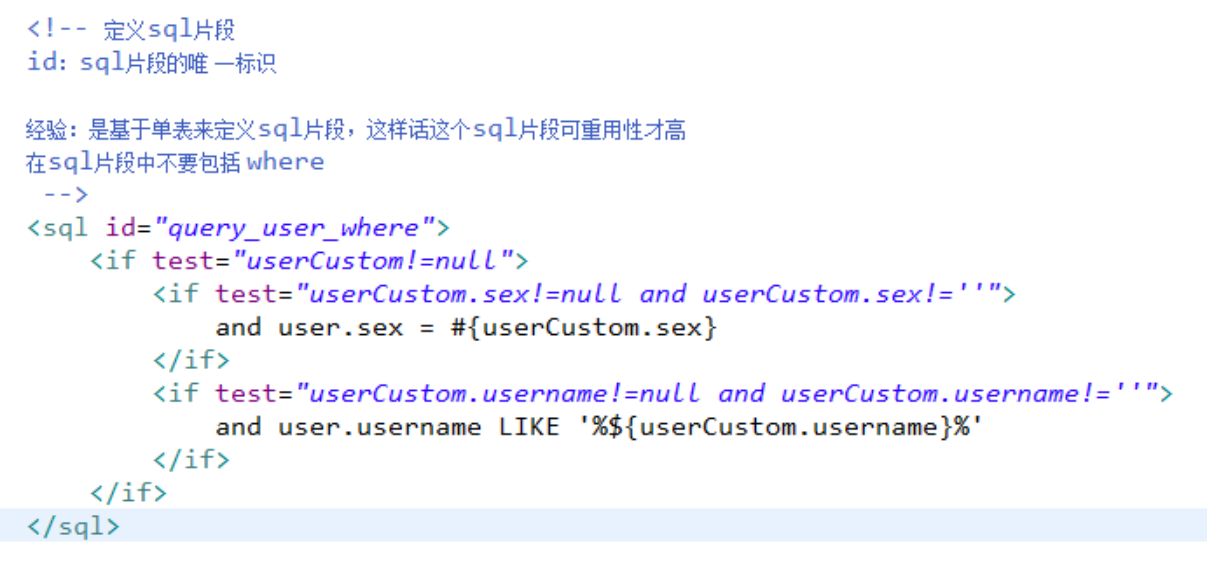
在mapper.xml中定义的statement中引用sql片段:
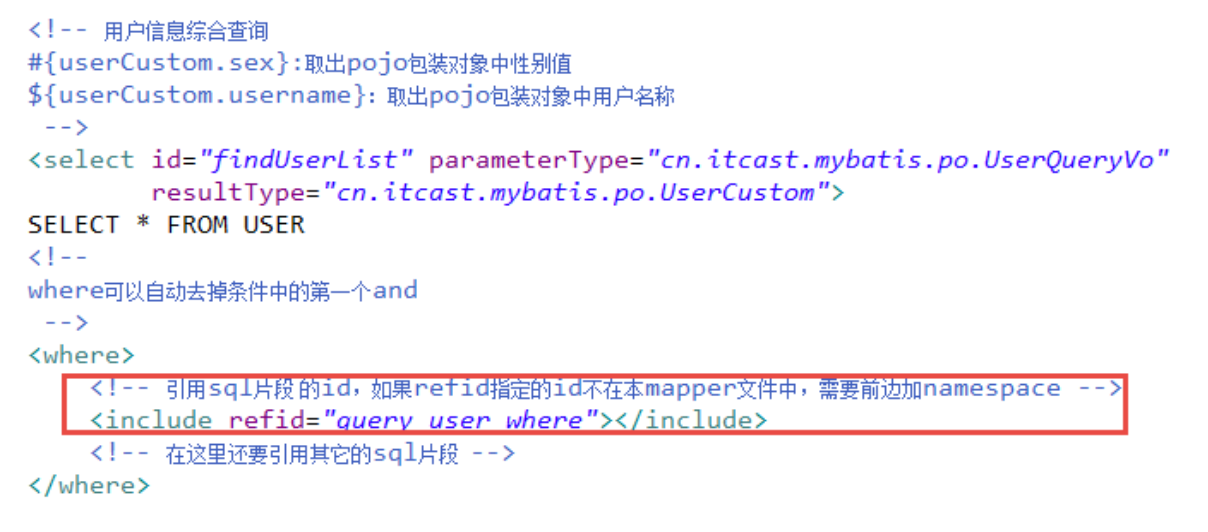
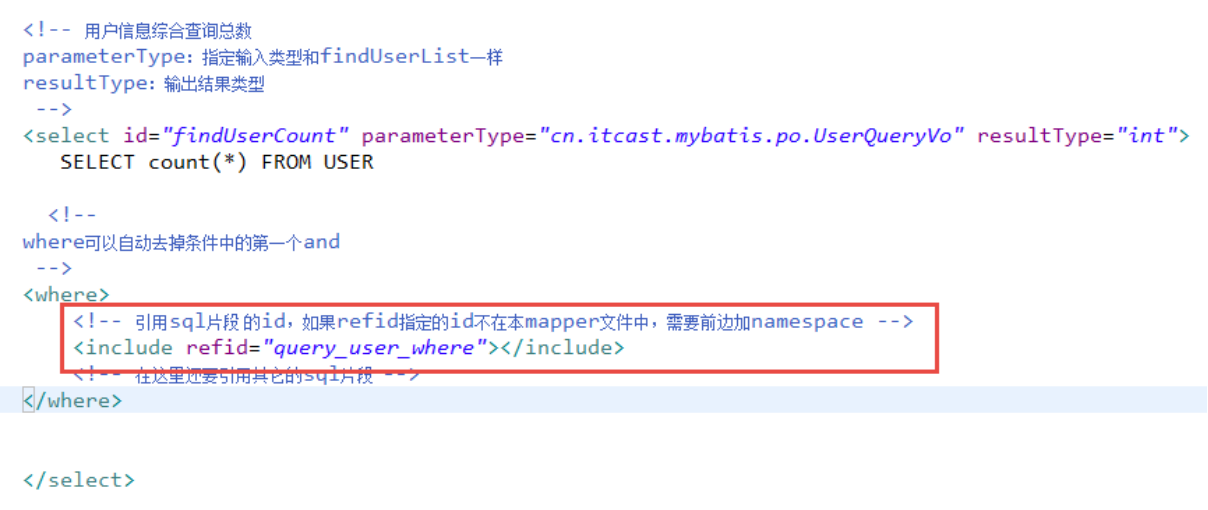
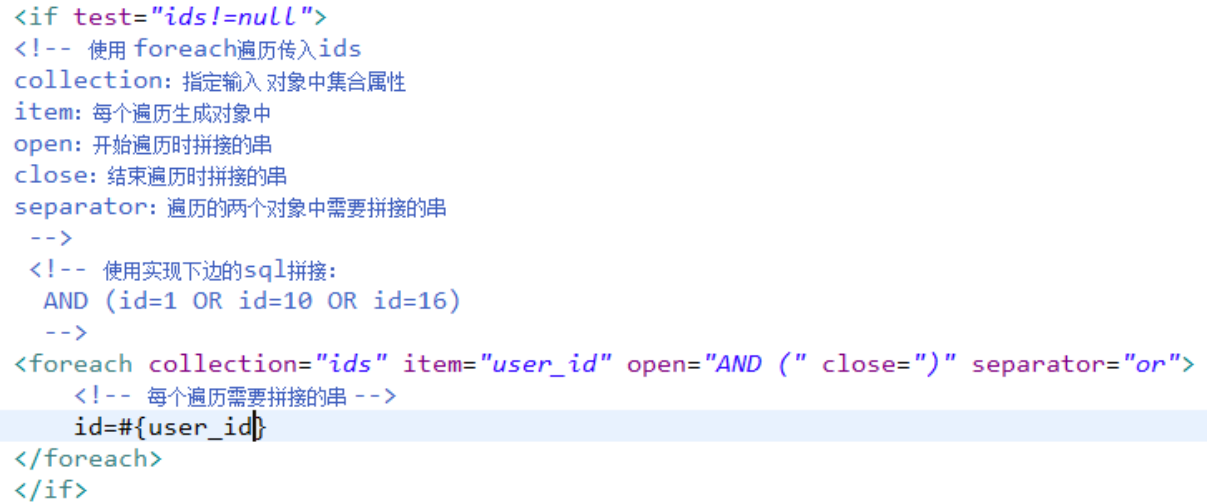
向sql传递数组或List,mybatis使用foreach解析
foreach的参数:
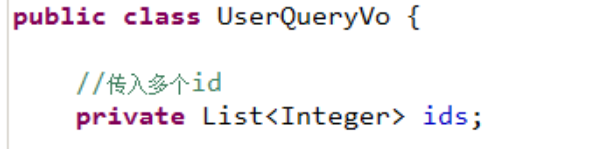
在用户查询列表和查询总数的statement中增加多个id输入查询。
sql语句如下:
两种方法:
SELECT * FROM USER WHERE id=1 OR id=10 OR id=16
SELECT * FROM USER WHERE id IN(1,10,16)
WHERE id=1 OR id=10 OR id=16
在查询条件中,查询条件定义成一个sql片段,需要修改sql片段。
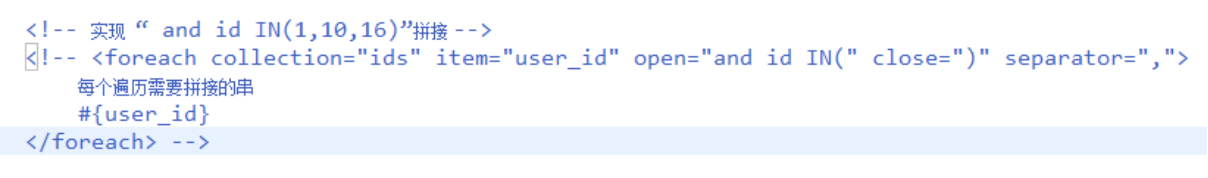
映射文件UserMapper.xml
<delete id="deleteBatch" parameterType="Integer">
delete from user where id in
<foreach collection="array" open="(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>Dao文件
public interface UserDao {
public void delete(Integer[] ids);
}
调用Controller
public void delete(Integer[] ids) {
userDao.delete(ids);
}
映射文件UserMapper.xml
<delete id="deleteBatch" parameterType="Integer">
delete from user
where id in
<foreach collection="list" open="(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>
Dao文件
public interface UserDao {
public void delete(List<Integer> ids);
}调用Controller
@RequestMapping("/deletebatch")
public String deleteBatch(Integer[] id){
List<Integer> paraList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<id.length;i++){
paraList.add(id[i]);
}
userService.delete(paraList);
return "redirect:/user/list";
}
映射文件UserMapper.xml
//参数类型可以是map也可以是hashmap
<delete id="changeState" parameterType="map">
update contract_c
set STATE=#{state}
where CONTRACT_ID in
<foreach collection="ids" open="(" close=")" item="id" separator=",">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>Dao文件
public void changeState(Map map) {
this.getSqlSession().update(this.getNs() + "changeState", map);
}调用Controller
@RequestMapping("/submit.action")
public String submit(String[] id){
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("state", 1);
map.put("ids", id);
localService.changeState(map);
return "redirect:/cargo/contract/list.action";
}
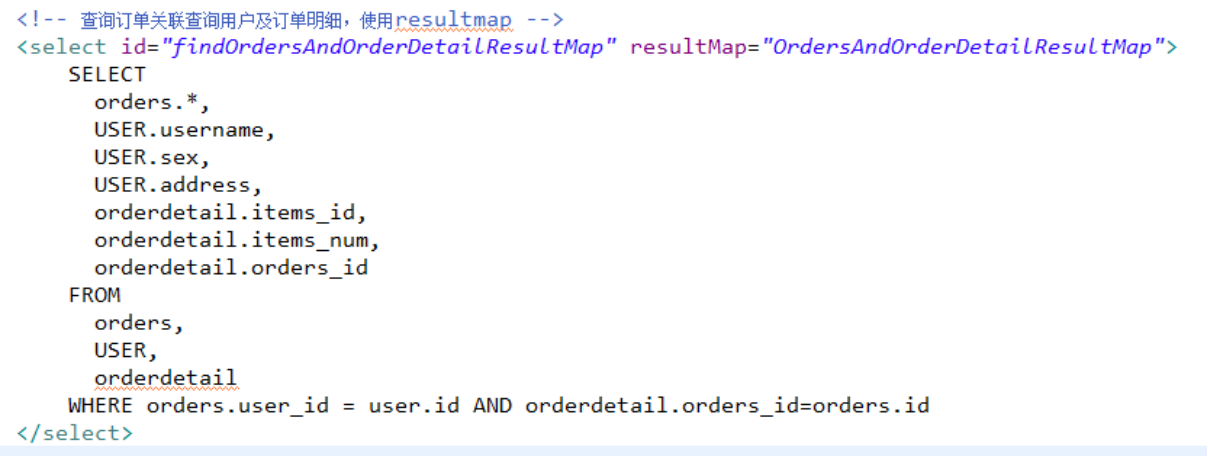
查询订单及订单明细的信息。
确定主查询表:订单表
确定关联查询表:订单明细表
在一对一查询基础上添加订单明细表关联即可。
SELECT
orders.*,
USER.username,
USER.sex,
USER.address,
orderdetail.id orderdetail_id,
orderdetail.items_id,
orderdetail.items_num,
orderdetail.orders_id
FROM
orders,
USER,
orderdetail
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id AND orderdetail.orders_id=orders.id使用resultType将上边的 查询结果映射到pojo中,订单信息的就是重复。
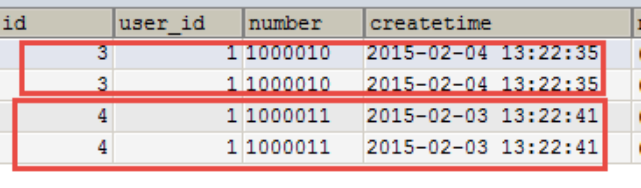
要求:
对orders映射不能出现重复记录。
在orders.java类中添加List<orderDetail> orderDetails属性。
最终会将订单信息映射到orders中,订单所对应的订单明细映射到orders中的orderDetails属性中。
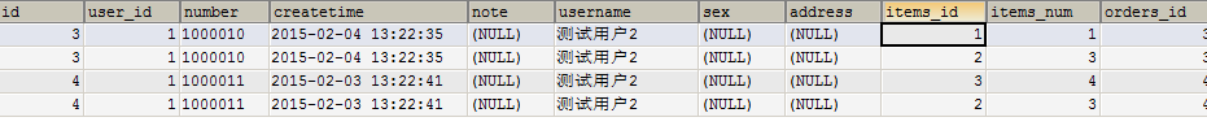
映射成的orders记录数为两条(orders信息不重复)
每个orders中的orderDetails属性存储了该 订单所对应的订单明细。
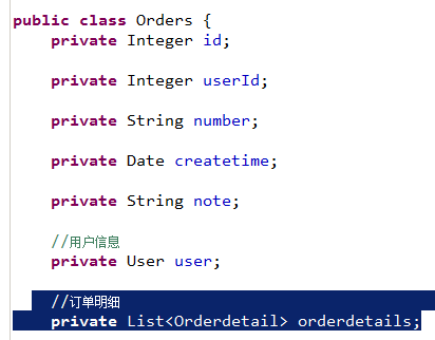
<resultMap id="唯一的标识" type="映射的pojo对象">
<id column="表的主键字段或查询语句中的别名字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="映射pojo对象的主键属性" />
<result column="表的一个字段(可以为任意表的一个字段)" jdbcType="字段类型" property="映射到pojo对象的一个属性"/>
<collection property="pojo的集合属性" ofType="集合中的pojo对象">
<id column="集合中pojo对象对应的表的主键字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="集合中pojo对象的主键属性" />
<result column="可以为任意表的字段" jdbcType="字段类型" property="集合中的pojo对象的属性" />
</collection>
</resultMap>
<!-- 订单及订单明细的resultMap
使用extends继承,不用在中配置订单信息和用户信息的映射
-->
<resultMap type="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders" id="OrdersAndOrderDetailResultMap" extends="OrdersUserResultMap">
<!-- 订单信息 -->
<!-- 用户信息 -->
<!-- 使用extends继承,不用在中配置订单信息和用户信息的映射 -->
<!-- 订单明细信息
一个订单关联查询出了多条明细,要使用collection进行映射
collection:对关联查询到多条记录映射到集合对象中
property:将关联查询到多条记录映射到cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders哪个属性
ofType:指定映射到list集合属性中pojo的类型
-->
<collection property="orderdetails" ofType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orderdetail">
<!-- id:订单明细唯 一标识
property:要将订单明细的唯 一标识 映射到cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orderdetail的哪个属性
-->
<id column="orderdetail_id" property="id"/>
<result column="items_id" property="itemsId"/>
<result column="items_num" property="itemsNum"/>
<result column="orders_id" property="ordersId"/>
</collection>
</resultMap>
mybatis使用resultMap的collection对关联查询的多条记录映射到一个list集合属性中。
使用resultType实现:
将订单明细映射到orders中的orderdetails中,需要自己处理,使用双重循环遍历,去掉重复记录,将订单明细放在orderdetails中。
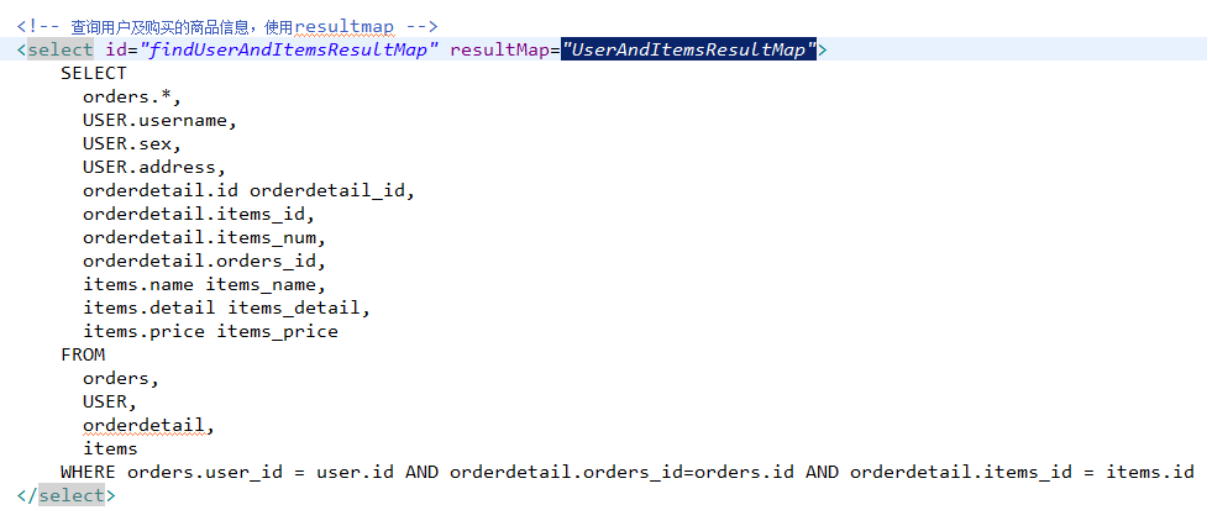
查询用户及用户购买商品信息。
查询主表是:用户表
关联表:由于用户和商品没有直接关联,通过订单和订单明细进行关联,所以关联表:
orders、orderdetail、items
SELECT
orders.*,
USER.username,
USER.sex,
USER.address,
orderdetail.id orderdetail_id,
orderdetail.items_id,
orderdetail.items_num,
orderdetail.orders_id,
items.name items_name,
items.detail items_detail,
items.price items_price
FROM
orders,
USER,
orderdetail,
items
WHERE orders.user_id = user.id AND orderdetail.orders_id=orders.id AND orderdetail.items_id = items.id
将用户信息映射到user中。
在user类中添加订单列表属性List<Orders> orderslist,将用户创建的订单映射到orderslist
在Orders中添加订单明细列表属性List<OrderDetail>orderdetials,将订单的明细映射到orderdetials
在OrderDetail中添加Items属性,将订单明细所对应的商品映射到Items
<!-- 查询用户及购买的商品 -->
<resultMap type="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User" id="UserAndItemsResultMap">
<!-- 用户信息 -->
<id column="user_id" property="id"/>
<result column="username" property="username"/>
<result column="sex" property="sex"/>
<result column="address" property="address"/>
<!-- 订单信息
一个用户对应多个订单,使用collection映射
-->
<collection property="ordersList" ofType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders">
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="user_id" property="userId"/>
<result column="number" property="number"/>
<result column="createtime" property="createtime"/>
<result column="note" property="note"/>
<!-- 订单明细一个订单包括 多个明细 -->
<collection property="orderdetails" ofType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orderdetail">
<id column="orderdetail_id" property="id"/>
<result column="items_id" property="itemsId"/>
<result column="items_num" property="itemsNum"/>
<result column="orders_id" property="ordersId"/>
<!-- 商品信息
一个订单明细对应一个商品
-->
<association property="items" javaType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Items">
<id column="items_id" property="id"/>
<result column="items_name" property="name"/>
<result column="items_detail" property="detail"/>
<result column="items_price" property="price"/>
</association>
</collection>
</collection>
</resultMap>
将查询用户购买的商品信息明细清单,(用户名、用户地址、购买商品名称、购买商品时间、购买商品数量)
针对上边的需求就使用resultType将查询到的记录映射到一个扩展的pojo中,很简单实现明细清单的功能。
一对多是多对多的特例,如下需求:
查询用户购买的商品信息,用户和商品的关系是多对多关系。
需求1:
查询字段:用户账号、用户名称、用户性别、商品名称、商品价格(最常见)
企业开发中常见明细列表,用户购买商品明细列表,
使用resultType将上边查询列映射到pojo输出。
需求2:
查询字段:用户账号、用户名称、购买商品数量、商品明细(鼠标移上显示明细)
使用resultMap将用户购买的商品明细列表映射到user对象中。
总结:
使用resultMap是针对那些对查询结果映射有特殊要求的功能,,比如特殊要求映射成list中包括 多个list。
resultMap可以实现延迟加载,resultType无法实现延迟加载。
resultType:
作用:
将查询结果按照sql列名pojo属性名一致性映射到pojo中。
场合:
常见一些明细记录的展示,比如用户购买商品明细,将关联查询信息全部展示在页面时,此时可直接使用resultType将每一条记录映射到pojo中,在前端页面遍历list(list中是pojo)即可。
resultMap:
使用association和collection完成一对一和一对多高级映射(对结果有特殊的映射要求)。
association:
作用:
将关联查询信息映射到一个pojo对象中。
场合:
为了方便查询关联信息可以使用association将关联订单信息映射为用户对象的pojo属性中,比如:查询订单及关联用户信息。
使用resultType无法将查询结果映射到pojo对象的pojo属性中,根据对结果集查询遍历的需要选择使用resultType还是resultMap。
collection:
作用:
将关联查询信息映射到一个list集合中。
场合:
为了方便查询遍历关联信息可以使用collection将关联信息映射到list集合中,比如:查询用户权限范围模块及模块下的菜单,可使用collection将模块映射到模块list中,将菜单列表映射到模块对象的菜单list属性中,这样的作的目的也是方便对查询结果集进行遍历查询。
如果使用resultType无法将查询结果映射到list集合中。
resultMap可以实现高级映射(使用association、collection实现一对一及一对多映射),association、collection具备延迟加载功能。
需求:
如果查询订单并且关联查询用户信息。如果先查询订单信息即可满足要求,当我们需要查询用户信息时再查询用户信息。把对用户信息的按需去查询就是延迟加载。
延迟加载:先从单表查询、需要时再从关联表去关联查询,大大提高 数据库性能,因为查询单表要比关联查询多张表速度要快。
查询订单并且关联查询用户信息
需要定义两个mapper的方法对应的statement。
1、只查询订单信息
SELECT * FROM orders
在查询订单的statement中使用association去延迟加载(执行)下边的satatement(关联查询用户信息)
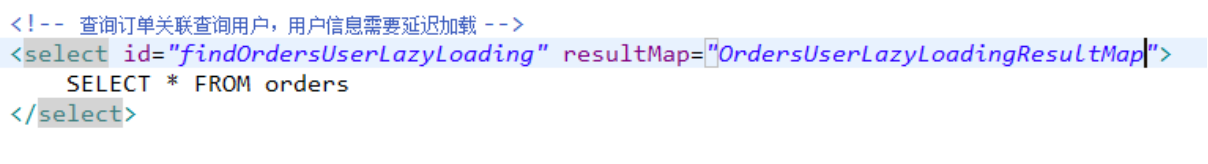
2、关联查询用户信息
通过上边查询到的订单信息中user_id去关联查询用户信息
使用UserMapper.xml中的findUserById

上边先去执行findOrdersUserLazyLoading,当需要去查询用户的时候再去执行findUserById,通过resultMap的定义将延迟加载执行配置起来。
使用association中的select指定延迟加载去执行的statement的id。
<!-- 延迟加载的resultMap -->
<resultMap type="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.Orders" id="OrdersUserLazyLoadingResultMap">
<!--对订单信息进行映射配置 -->
<id column="id" property="id"/>
<result column="user_id" property="userId"/>
<result column="number" property="number"/>
<result column="createtime" property="createtime"/>
<result column="note" property="note"/>
<!-- 实现对用户信息进行延迟加载
select:指定延迟加载需要执行的statement的id(是根据user_id查询用户信息的statement)
要使用userMapper.xml中findUserById完成根据用户id(user_id)用户信息的查询,如果findUserById不在本mapper中需要前边加namespace
column:订单信息中关联用户信息查询的列,是user_id
关联查询的sql理解为:
SELECT orders.*,
(SELECT username FROM USER WHERE orders.user_id = user.id)username,
(SELECT sex FROM USER WHERE orders.user_id = user.id)sex
FROM orders
-->
<association property="user" javaType="cn.itcast.mybatis.po.User"
select="cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper.UserMapper.findUserById" column="user_id">
<!-- 实现对用户信息进行延迟加载 -->
</association>
</resultMap>
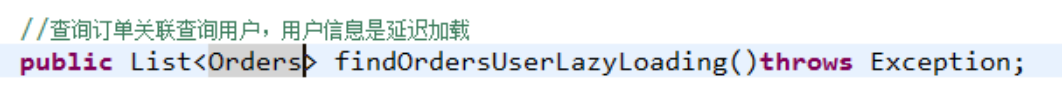
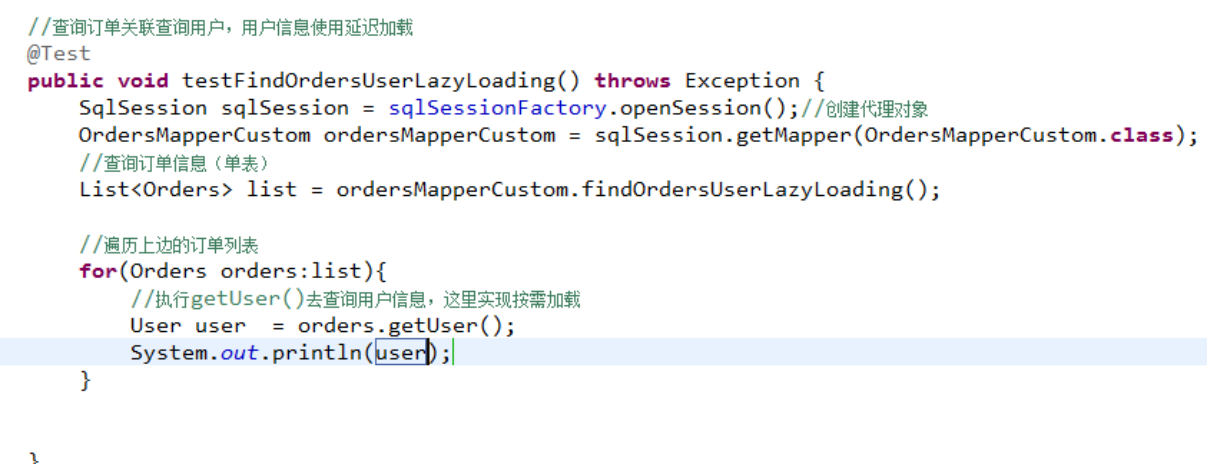
1、执行上边mapper方法(findOrdersUserLazyLoading),内部去调用cn.itcast.mybatis.mapper.OrdersMapperCustom中的findOrdersUserLazyLoading只查询orders信息(单表)。
2、在程序中去遍历上一步骤查询出的List<Orders>,当我们调用Orders中的getUser方法时,开始进行延迟加载。
3、延迟加载,去调用UserMapper.xml中findUserbyId这个方法获取用户信息。
mybatis默认没有开启延迟加载,需要在SqlMapConfig.xml中setting配置。
在mybatis核心配置文件中配置:
lazyLoadingEnabled、aggressiveLazyLoading
|
设置项 |
描述 |
允许值 |
默认值 |
|
lazyLoadingEnabled |
全局性设置懒加载。如果设为‘false’,则所有相关联的都会被初始化加载。 |
true | false |
false |
|
aggressiveLazyLoading |
当设置为‘true’的时候,懒加载的对象可能被任何懒属性全部加载。否则,每个属性都按需加载。 |
true | false |
true |
在SqlMapConfig.xml中配置:

不使用mybatis提供的association及collection中的延迟加载功能,如何实现延迟加载??
实现方法如下:
定义两个mapper方法:
1、查询订单列表
2、根据用户id查询用户信息
实现思路:
先去查询第一个mapper方法,获取订单信息列表
在程序中(service),按需去调用第二个mapper方法去查询用户信息。
总之:
使用延迟加载方法,先去查询简单的sql(最好单表,也可以关联查询),再去按需要加载关联查询的其它信息。
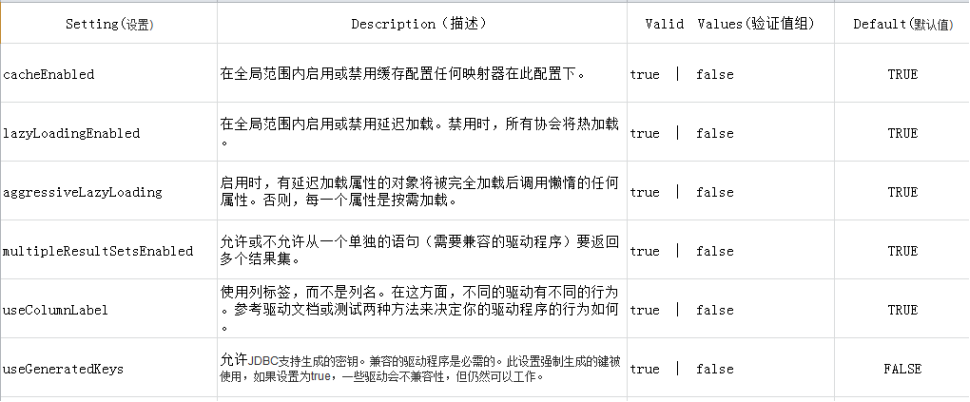
|
Setting(设置) |
Description(描述) |
Valid Values(验证值组) |
Default(默认值) |
|
cacheEnabled |
在全局范围内启用或禁用缓存配置任何映射器在此配置下。 |
true | false |
TRUE |
|
lazyLoadingEnabled |
在全局范围内启用或禁用延迟加载。禁用时,所有协会将热加载。 |
true | false |
TRUE |
|
aggressiveLazyLoading |
启用时,有延迟加载属性的对象将被完全加载后调用懒惰的任何属性。否则,每一个属性是按需加载。 |
true | false |
TRUE |
|
multipleResultSetsEnabled |
允许或不允许从一个单独的语句(需要兼容的驱动程序)要返回多个结果集。 |
true | false |
TRUE |
|
useColumnLabel |
使用列标签,而不是列名。在这方面,不同的驱动有不同的行为。参考驱动文档或测试两种方法来决定你的驱动程序的行为如何。 |
true | false |
TRUE |
|
useGeneratedKeys |
允许JDBC支持生成的密钥。兼容的驱动程序是必需的。此设置强制生成的键被使用,如果设置为true,一些驱动会不兼容性,但仍然可以工作。 |
true | false |
FALSE |
|
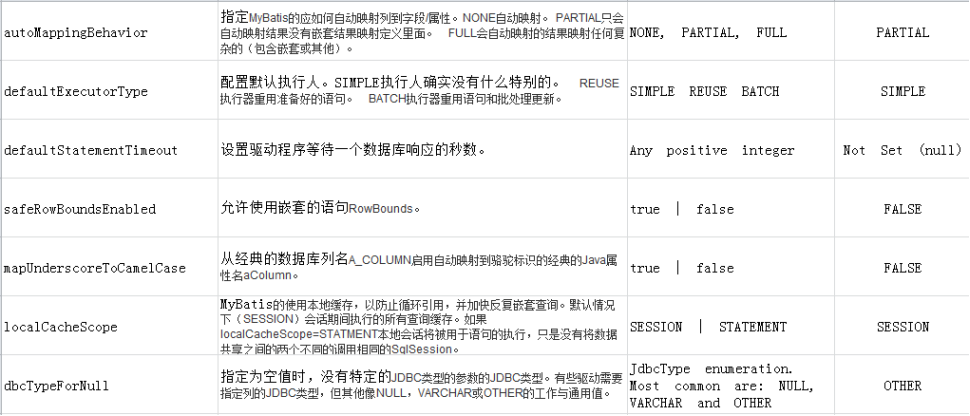
autoMappingBehavior |
指定MyBatis的应如何自动映射列到字段/属性。NONE自动映射。 PARTIAL只会自动映射结果没有嵌套结果映射定义里面。 FULL会自动映射的结果映射任何复杂的(包含嵌套或其他)。 |
NONE, PARTIAL, FULL |
PARTIAL |
|
defaultExecutorType |
配置默认执行人。SIMPLE执行人确实没有什么特别的。 REUSE执行器重用准备好的语句。 BATCH执行器重用语句和批处理更新。 |
SIMPLE REUSE BATCH |
SIMPLE |
|
defaultStatementTimeout |
设置驱动程序等待一个数据库响应的秒数。 |
Any positive integer |
Not Set (null) |
|
safeRowBoundsEnabled |
允许使用嵌套的语句RowBounds。 |
true | false |
FALSE |
|
mapUnderscoreToCamelCase |
从经典的数据库列名A_COLUMN启用自动映射到骆驼标识的经典的Java属性名aColumn。 |
true | false |
FALSE |
|
localCacheScope |
MyBatis的使用本地缓存,以防止循环引用,并加快反复嵌套查询。默认情况下(SESSION)会话期间执行的所有查询缓存。如果localCacheScope=STATMENT本地会话将被用于语句的执行,只是没有将数据共享之间的两个不同的调用相同的SqlSession。 |
SESSION | STATEMENT |
SESSION |
|
dbcTypeForNull |
指定为空值时,没有特定的JDBC类型的参数的JDBC类型。有些驱动需要指定列的JDBC类型,但其他像NULL,VARCHAR或OTHER的工作与通用值。 |
JdbcType enumeration. Most common are: NULL, VARCHAR and OTHER |
OTHER |
|
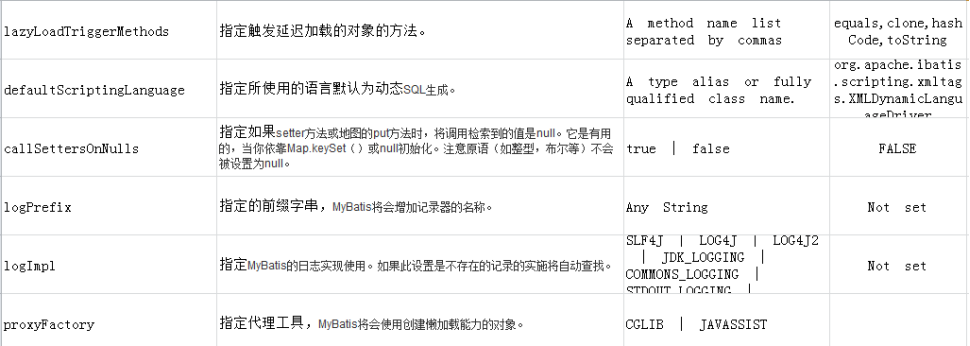
lazyLoadTriggerMethods |
指定触发延迟加载的对象的方法。 |
A method name list separated by commas |
equals,clone,hashCode,toString |
|
defaultScriptingLanguage |
指定所使用的语言默认为动态SQL生成。 |
A type alias or fully qualified class name. |
org.apache.ibatis.scripting.xmltags.XMLDynamicLanguageDriver |
|
callSettersOnNulls |
指定如果setter方法或地图的put方法时,将调用检索到的值是null。它是有用的,当你依靠Map.keySet()或null初始化。注意原语(如整型,布尔等)不会被设置为null。 |
true | false |
FALSE |
|
logPrefix |
指定的前缀字串,MyBatis将会增加记录器的名称。 |
Any String |
Not set |
|
logImpl |
指定MyBatis的日志实现使用。如果此设置是不存在的记录的实施将自动查找。 |
SLF4J | LOG4J | LOG4J2 | JDK_LOGGING | COMMONS_LOGGING | STDOUT_LOGGING | NO_LOGGING |
Not set |
|
proxyFactory |
指定代理工具,MyBatis将会使用创建懒加载能力的对象。 |
CGLIB | JAVASSIST |
|
@Param注解的作用是给参数命名,参数命名后就能根据名字得到参数值,正确的将参数传入sql语句中
public Student select(@Param("aaaa") String name,@Param("bbbb")int class_id);
where s_name= #{aaaa} and class_id = #{bbbb}
使用@Param注解来声明参数时,如果使用 #{} 或 ${} 的方式都可以。
你不使用@Param注解来声明参数时,必须使用使用 #{}方式。如果使用 ${} 的方式,会报错。
不使用@Param注解时,参数只能有一个,并且是Javabean。
服务器启动的时候
数据库连接池的主要操作如下:
(1)建立数据库连接池对象(服务器启动)。
(2)按照事先指定的参数创建初始数量的数据库连接(即:空闲连接数)。
(3)对于一个数据库访问请求,直接从连接池中得到一个连接。如果数据库连接池对象中没有空闲的连接,且连接数没有达到最大(即:最大活跃连接数),创建一个新的数据库连接。
(4)存取数据库。
(5)关闭数据库,释放所有数据库连接(此时的关闭数据库连接,并非真正关闭,而是将其放入空闲队列中。如实际空闲连接数大于初始空闲连接数则释放连接)
(6)释放数据库连接池对象(服务器停止、维护期间,释放数据库连接池对象,并释放所有连接)。
|
< |
<= |
> |
>= |
& |
' |
" |
|
< |
<= |
> |
>= |
& |
' |
" |
批量修改需要再jdbc连接加上&allowMultiQueries=true
allowMultiQueries=true是一个MySQL JDBC连接参数,用于控制是否允许在一个SQL语句中执行多个查询。当这个参数被设置为true时,意味着你可以通过分号(;)分隔,在单个Statement或PreparedStatement对象中执行多个SQL查询。这对于需要在一次数据库交互中执行一系列独立查询的场景非常有用,比如批处理插入或多表更新等操作。
批量更新三种方式
foreach嵌套update
<update id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List">
<foreach collection="list" item="item" index="index" open="" close="" separator=";">
update tableName
<set>
name=${item.name},
name2=${item.name2}
</set>
where id = ${item.id}
</foreach>
</update>
update嵌套foreach,用when then
<update id="updateBatch" parameterType="java.util.List">
update tableName
<trim prefix="set" suffixOverrides=",">
<trim prefix="c_name =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="cus">
<if test="cus.name!=null">
when id=#{cus.id} then #{cus.name}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
<trim prefix="c_age =case" suffix="end,">
<foreach collection="list" item="cus">
<if test="cus.age!=null">
when id=#{cus.id} then #{cus.age}
</if>
</foreach>
</trim>
</trim>
<where>
<foreach collection="list" separator="or" item="cus">
id = #{cus.id}
</foreach>
</where>
</update>
<update id="updateDeptChildren" parameterType="java.util.List">
update sys_dept set ancestors =
<foreach collection="depts" item="item" index="index"
separator=" " open="case dept_id" close="end">
when #{item.deptId} then #{item.ancestors}
</foreach>
,
status =
<foreach collection="depts" item="item" index="index"
separator=" " open="case dept_id" close="end">
when #{item.deptId} then #{item.status}
</foreach>
,
update_by =
<foreach collection="depts" item="item" index="index"
separator=" " open="case dept_id" close="end">
when #{item.deptId} then #{item.updateBy}
</foreach>
, update_time = sysdate()
where dept_id in
<foreach collection="depts" item="item" index="index"
separator="," open="(" close=")">
#{item.deptId}
</foreach>
</update>
方式三:
临时改表sqlSessionFactory的属性,实现批量提交的java,但无法返回受影响数量。
|
public int updateBatch(List<Object> list){ if(list ==null || list.size() <= 0){ return -1; } SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = SpringContextUtil.getBean("sqlSessionFactory"); SqlSession sqlSession = null; try { sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(ExecutorType.BATCH,false); Mapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(Mapper.class); int batchCount = 1000;//提交数量,到达这个数量就提交 for (int index = 0; index < list.size(); index++) { Object obj = list.get(index); mapper.updateInfo(obj); if(index != 0 && index%batchCount == 0){ sqlSession.commit(); } } sqlSession.commit(); return 0; }catch (Exception e){ sqlSession.rollback(); return -2; }finally { if(sqlSession != null){ sqlSession.close(); } }
} |
方式一 需要修改mysql的连接url,让全局支持多sql执行,不太安全
方式二 当数据量大的时候 ,效率明显降低
方式三 需要自己控制,自己处理,一些隐藏的问题无法发现。
|
<insert id ="insertCodeBatch" parameterType="java.util.List" > insert into redeem_code (bach_id, code, type, facevalue,create_user,create_time) values <foreach collection ="list" item="reddemCode" index= "index" separator =","> ( #{reddemCode.batchId}, #{reddemCode.code}, #{reddemCode.type}, #{reddemCode.facevalue}, #{reddemCode.createUser}, #{reddemCode.createTime} ) </foreach > </insert > |
|
<!-- 插入或更新资料热度值 --> <insert id="saveContentHot" parameterType="com.dongao.materials.front.domain.ContentHot"> INSERT INTO ec_mat_content_hot (content_id,hot) VALUES(#{contentId}, #{hot}) ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE content_id = VALUES(content_id), hot = hot +VALUES(hot) </insert>
<insert id="bachSaveContentHot" parameterType="com.dongao.materials.front.domain.ContentHot"> INSERT INTO ec_mat_content_hot (content_id,hot) VALUES <foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list" separator=","> ( #{item.contentId}, #{item.hot} ) </foreach> ON DUPLICATE KEY UPDATE content_id = VALUES(content_id), hot = hot +VALUES(hot) </insert> |
利用choose when otherwise结构
|
<select id="selectHotContents" parameterType="com.dongao.materials.front.domain.ContentQueryVo" resultType="com.dongao.materials.front.domain.ContentResultVo" > <choose> <when test="tagId != null"> select c.id, c.title, c.description, c.category_id categoryId, c.subject_id subjectId, c.classific_id classificId, c.is_special isSpecial, c.status, c.file_type fileType, c.total_page totalPage, c.free_page freePage, c.download_base downloadBase, c.glance_base glanceBase, c.doc_size, c.doc_count docCount, c.recommend_status recommendStatus, c.recommend_site recommendSite, c.sort, c.creator, c.create_time createTime, c.updator, c.update_time updateTime ,sum(c.download_base*10 + c.glance_base*7 + IFNULL(ch.hot,0)) chot from ec_mat_content_tag ct , ec_mat_content c left join ec_mat_content_hot ch on c.id = ch.content_id </when> <otherwise> select c.id, c.title, c.description, c.category_id categoryId, c.subject_id subjectId, c.classific_id classificId, c.is_special isSpecial, c.status, c.file_type fileType, c.total_page totalPage, c.free_page freePage, c.download_base downloadBase, c.glance_base glanceBase, c.doc_size, c.doc_count docCount, c.recommend_status recommendStatus, c.recommend_site recommendSite, c.sort, c.creator, c.create_time createTime, c.updator, c.update_time updateTime from ec_mat_content c left join ec_mat_content_hot ch on c.id = ch.content_id </otherwise> </choose> <where> c.status =1 and c.is_special = 0 <if test="categoryId != null "> and c.category_id = #{categoryId}</if> <if test="subjectId != null "> and c.subject_id = #{subjectId}</if> <if test="classificId != null "> and c.classific_id = #{classificId}</if> <if test="tagId != null "> and ct.tag_id = #{tagId} and ct.content_id = c.id</if> </where> group by c.id order by chot desc, c.update_time desc </select> |
### Cause: org.apache.ibatis.transaction.TransactionException: Error configuring AutoCommit. Your driver may not support getAutoCommit() or setAutoCommit(). Requested setting: false. Cause: com.mysql.jdbc.exceptions.jdbc4.CommunicationsException: The last packet successfully received from the server was 82,940,457 milliseconds ago. The last packet sent successfully to the server was 82,940,457 milliseconds ago. is longer than the server configured value of 'wait_timeout'. You should consider either expiring and/or testing connection validity before use in your application, increasing the server configured values for client timeouts, or using the Connector/J connection property 'autoReconnect=true' to avoid this problem.
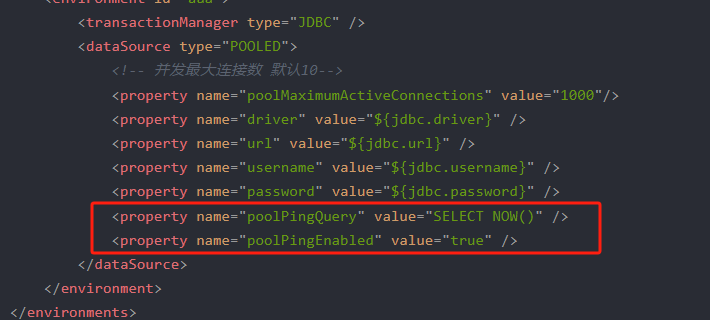
解决办法是在mybatis配置文件中加如下配置:
<property name="poolPingQuery" value="SELECT NOW()" />
<property name="poolPingEnabled" value="true" />