再玩亿关小游戏
444.26MB · 2025-11-02
查看集群状态:
GET /_cluster/health:获取集群的健康状态,如green(所有主分片和副本分片都可用)、yellow(所有主分片都可用,但并非所有副本分片都可用)或red(至少一个主分片不可用)。集群统计信息:返回分片号,存储大小,内存使用率,节点数,角色,操作系统和文件系统。
GET /_cluster/stats
{
"_nodes" : {
"total" : 3,
"successful" : 3,
"failed" : 0
},
"cluster_name" : "bussiness-test",
"cluster_uuid" : "I_Lq6O05SsK8yhnvhayK9A",
"timestamp" : 1721786317083,
"status" : "green",
"indices" : {
"count" : 296,
"shards" : {
"total" : 1593,
"primaries" : 1478,
"replication" : 0.07780784844384303,
"index" : {
"shards" : {
"min" : 1,
"max" : 12,
"avg" : 5.381756756756757
},
"primaries" : {
"min" : 1,
"max" : 12,
"avg" : 4.993243243243243
},
"replication" : {
"min" : 0.0,
"max" : 2.0,
"avg" : 0.19932432432432431
}
}
},
"docs" : {
"count" : 13468216875,
"deleted" : 2023500024
},
"store" : {
"size_in_bytes" : 6904887543190,
"reserved_in_bytes" : 0
},
"fielddata" : {
"memory_size_in_bytes" : 3593202744,
"evictions" : 0
},
"query_cache" : {
"memory_size_in_bytes" : 944900841,
"total_count" : 102075762493,
"hit_count" : 11992222707,
"miss_count" : 90083539786,
"cache_size" : 117641,
"cache_count" : 14249419,
"evictions" : 14131778
},
"completion" : {
"size_in_bytes" : 0
},
"segments" : {
"count" : 21468,
"memory_in_bytes" : 107327136,
"terms_memory_in_bytes" : 58626584,
"stored_fields_memory_in_bytes" : 12169280,
"term_vectors_memory_in_bytes" : 0,
"norms_memory_in_bytes" : 3473792,
"points_memory_in_bytes" : 0,
"doc_values_memory_in_bytes" : 33057480,
"index_writer_memory_in_bytes" : 141130640,
"version_map_memory_in_bytes" : 1864291,
"fixed_bit_set_memory_in_bytes" : 356787672,
"max_unsafe_auto_id_timestamp" : 1721779209050,
"file_sizes" : { }
},
"mappings" : {
"field_types" : [
{
"name" : "alias",
"count" : 1,
"index_count" : 1
},
{
"name" : "boolean",
"count" : 64,
"index_count" : 23
},
{
"name" : "date",
"count" : 697,
"index_count" : 202
},
{
"name" : "dense_vector",
"count" : 34,
"index_count" : 34
},
{
"name" : "double",
"count" : 537,
"index_count" : 62
},
{
"name" : "float",
"count" : 22,
"index_count" : 7
},
{
"name" : "geo_point",
"count" : 6,
"index_count" : 5
},
{
"name" : "half_float",
"count" : 47,
"index_count" : 8
},
{
"name" : "integer",
"count" : 560,
"index_count" : 187
},
{
"name" : "ip",
"count" : 2,
"index_count" : 1
},
{
"name" : "keyword",
"count" : 4911,
"index_count" : 270
},
{
"name" : "long",
"count" : 1358,
"index_count" : 153
},
{
"name" : "nested",
"count" : 97,
"index_count" : 45
},
{
"name" : "object",
"count" : 960,
"index_count" : 86
},
{
"name" : "text",
"count" : 1953,
"index_count" : 188
}
]
},
"analysis" : {
"char_filter_types" : [
{
"name" : "mapping",
"count" : 142,
"index_count" : 142
},
{
"name" : "stconvert",
"count" : 139,
"index_count" : 139
}
],
"tokenizer_types" : [ ],
"filter_types" : [
{
"name" : "common_grams",
"count" : 278,
"index_count" : 139
}
],
"analyzer_types" : [
{
"name" : "custom",
"count" : 290,
"index_count" : 143
}
],
"built_in_char_filters" : [
{
"name" : "html_strip",
"count" : 1,
"index_count" : 1
}
],
"built_in_tokenizers" : [
{
"name" : "ngram",
"count" : 6,
"index_count" : 3
},
{
"name" : "standard",
"count" : 284,
"index_count" : 143
}
],
"built_in_filters" : [
{
"name" : "asciifolding",
"count" : 1,
"index_count" : 1
},
{
"name" : "lowercase",
"count" : 289,
"index_count" : 142
}
],
"built_in_analyzers" : [
{
"name" : "english",
"count" : 1,
"index_count" : 1
},
{
"name" : "ik_max_word",
"count" : 1,
"index_count" : 1
},
{
"name" : "ik_smart",
"count" : 1,
"index_count" : 1
},
{
"name" : "ik_wenhai_new",
"count" : 71,
"index_count" : 24
},
{
"name" : "standard",
"count" : 22,
"index_count" : 3
}
]
},
"versions" : [
{
"version" : "7.11.1",
"index_count" : 296,
"primary_shard_count" : 1478,
"total_primary_bytes" : 6856685495729
}
]
},
"nodes" : {
"count" : {
"total" : 3,
"coordinating_only" : 0,
"data" : 3,
"data_cold" : 3,
"data_content" : 3,
"data_hot" : 3,
"data_warm" : 3,
"ingest" : 3,
"master" : 3,
"ml" : 3,
"remote_cluster_client" : 3,
"transform" : 3,
"voting_only" : 0
},
"versions" : [
"7.11.1"
],
"os" : {
"available_processors" : 96,
"allocated_processors" : 96,
"names" : [
{
"name" : "Linux",
"count" : 3
}
],
"pretty_names" : [
{
"pretty_name" : "CentOS Linux 7 (Core)",
"count" : 3
}
],
"mem" : {
"total_in_bytes" : 196197138432,
"free_in_bytes" : 1140416512,
"used_in_bytes" : 195056721920,
"free_percent" : 1,
"used_percent" : 99
}
},
"process" : {
"cpu" : {
"percent" : 5
},
"open_file_descriptors" : {
"min" : 13072,
"max" : 13377,
"avg" : 13247
}
},
"jvm" : {
"max_uptime_in_millis" : 42825336068,
"versions" : [
{
"version" : "15.0.1",
"vm_name" : "OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM",
"vm_version" : "15.0.1+9",
"vm_vendor" : "AdoptOpenJDK",
"bundled_jdk" : true,
"using_bundled_jdk" : true,
"count" : 3
}
],
"mem" : {
"heap_used_in_bytes" : 72470134976,
"heap_max_in_bytes" : 99857989632
},
"threads" : 897
},
"fs" : {
"total_in_bytes" : 26179817680896,
"free_in_bytes" : 18428823814144,
"available_in_bytes" : 17109359534080
},
"plugins" : [
{
"name" : "repository-s3",
"version" : "7.11.1",
"elasticsearch_version" : "7.11.1",
"java_version" : "1.8",
"description" : "The S3 repository plugin adds S3 repositories",
"classname" : "org.elasticsearch.repositories.s3.S3RepositoryPlugin",
"extended_plugins" : [ ],
"has_native_controller" : false,
"licensed" : false,
"type" : "isolated"
},
{
"name" : "analysis-stconvert",
"version" : "7.11.1",
"elasticsearch_version" : "7.11.1",
"java_version" : "1.8",
"description" : "STConvert is a analysis plugin that convert Chinese characters between traditional and simplified.",
"classname" : "org.elasticsearch.plugin.analysis.stconvert.AnalysisSTConvertPlugin",
"extended_plugins" : [ ],
"has_native_controller" : false,
"licensed" : false,
"type" : "isolated"
},
{
"name" : "ingest-attachment",
"version" : "7.11.1",
"elasticsearch_version" : "7.11.1",
"java_version" : "1.8",
"description" : "Ingest processor that uses Apache Tika to extract contents",
"classname" : "org.elasticsearch.ingest.attachment.IngestAttachmentPlugin",
"extended_plugins" : [ ],
"has_native_controller" : false,
"licensed" : false,
"type" : "isolated"
},
{
"name" : "analysis-ik",
"version" : "7.11.1",
"elasticsearch_version" : "7.11.1",
"java_version" : "1.8",
"description" : "IK Analyzer for Elasticsearch",
"classname" : "org.elasticsearch.plugin.analysis.ik.AnalysisIkPlugin",
"extended_plugins" : [ ],
"has_native_controller" : false,
"licensed" : false,
"type" : "isolated"
},
{
"name" : "sql",
"version" : "7.11.1.0",
"elasticsearch_version" : "7.11.1",
"java_version" : "1.8",
"description" : "Query elasticsearch using SQL",
"classname" : "org.elasticsearch.plugin.nlpcn.SqlPlug",
"extended_plugins" : [ ],
"has_native_controller" : false,
"licensed" : false,
"type" : "isolated"
}
],
"network_types" : {
"transport_types" : {
"security4" : 3
},
"http_types" : {
"security4" : 3
}
},
"discovery_types" : {
"zen" : 3
},
"packaging_types" : [
{
"flavor" : "default",
"type" : "tar",
"count" : 3
}
],
"ingest" : {
"number_of_pipelines" : 6,
"processor_stats" : {
"attachment" : {
"count" : 0,
"failed" : 0,
"current" : 0,
"time_in_millis" : 0
},
"enrich" : {
"count" : 1,
"failed" : 0,
"current" : 0,
"time_in_millis" : 30
},
"gsub" : {
"count" : 0,
"failed" : 0,
"current" : 0,
"time_in_millis" : 0
},
"remove" : {
"count" : 2,
"failed" : 0,
"current" : 0,
"time_in_millis" : 3
},
"script" : {
"count" : 0,
"failed" : 0,
"current" : 0,
"time_in_millis" : 0
}
}
}
}
}查看集群中的节点:
GET /_cat/nodes?v:列出集群中的所有节点及其相关信息。ip heap.percent ram.percent cpu load_1m load_5m load_15m node.role master name
172.16.30.3 66 98 0 0.12 0.33 0.36 cdhilmrstw * 172.16.30.3
172.16.30.2 50 86 0 0.25 0.20 0.22 cdhilmrstw - 172.16.30.2
172.16.30.4 65 98 1 0.51 0.44 0.37 cdhilrstw - 172.16.30.4-02
172.16.30.3 72 98 1 0.12 0.33 0.36 cdhilrstw - 172.16.30.3-02
172.16.30.2 47 86 0 0.25 0.20 0.22 cdhilrstw - 172.16.30.2-02
172.16.30.4 64 98 1 0.51 0.44 0.37 cdhilmrstw - 172.16.30.4查询es的版本
GET /
{
"name" : "172.16.30.2",
"cluster_name" : "bussiness-test",
"cluster_uuid" : "I_Lq6O05SsK8yhnvhayK9A",
"version" : {
"number" : "7.11.1",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "tar",
"build_hash" : "ff17057114c2199c9c1bbecc727003a907c0db7a",
"build_date" : "2021-02-15T13:44:09.394032Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "8.7.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "6.8.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "6.0.0-beta1"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}查看有哪些索引:
GET /_cat/indices?v创建索引:
PUT /index_name:创建一个名为index_name的新索引。通常,你会在请求体中定义索引的映射(即字段类型和设置)。删除索引:
DELETE /index_name:删除名为index_name的索引。查看索引映射:
GET /index_name/_mapping:获取名为index_name的索引的映射定义。查看索引设置:
GET /index_name/_settings:获取名为index_name的索引的设置信息。关闭索引:
POST /index_name/_close:关闭名为index_name的索引,使其不再接受读写请求。打开索引:
POST /index_name/_open:重新打开之前关闭的索引。刷新索引:
POST /index_name/_refresh:强制刷新一个或多个索引,使最近的更改对搜索可见。查看索引的分片和副本状态:
GET /index_name/_shards:获取有关索引的分片和副本的详细信息。添加字段:
PUT /your_index/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"new_keyword_field": {
"type": "keyword"
}
}
}查看索引别名:
GET /<index_name>/_alias添加索引别名:
场景 1:添加一个别名到一个索引
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "myindex",
"alias": "myalias"
}
}
]
}
添加带过滤条件的别名(Filter)
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{
"add": {
"index": "myindex",
"alias": "active_users",
"filter": {
"term": {
"status": "active"
}
}
}
}
]
}
添加多个别名到同一个索引
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{ "add": { "index": "myindex", "alias": "alias1" }},
{ "add": { "index": "myindex", "alias": "alias2" }}
]
}
同时操作多个索引和别名
POST /_aliases
{
"actions": [
{ "add": { "index": "myindex", "alias": "alias1" }},
{ "add": { "index": "otherindex", "alias": "alias2" }}
]
}
POST /index_name/_doc/ 或 PUT /index_name/_doc/document_id:索引一个新文档或更新一个现有文档。你需要在请求体中提供文档的内容。PUT /my_index/_doc/1
{
"title": "Document 1",
"content": "This is the content of document 1.",
"tags": ["tag1", "tag2"]
}添加字段:
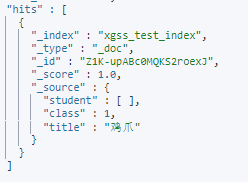
POST /xgss_test_index/_update/Z1K-upABc0MQKS2roexJ
{
"doc": {
"name" : "小脸脸"
}
}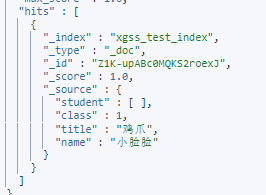
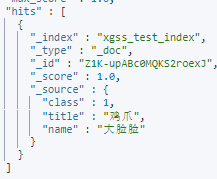
覆盖字段:跟字段名相同即可
POST /xgss_test_index/_update/Z1K-upABc0MQKS2roexJ
{
"doc": {
"name" : "大脸脸"
}
}
POST /xgss_test_index/_update/Z1K-upABc0MQKS2roexJ
{
"doc": {
"student" : [
{
"name" : "王五",
"age":1
},
{
"name" : "马六",
"age":1
}
]
}
}
POST /xgss_test_index/_update/Z1K-upABc0MQKS2roexJ
{
"doc": {
"student" : []
}
}
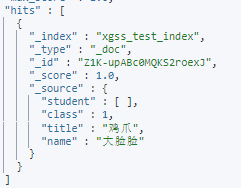
删除字段
POST xgss_test_index/_update/Z1K-upABc0MQKS2roexJ
{
"script": {
"source": "ctx._source.remove('student')",
"lang": "painless"
}
}删除前
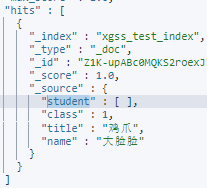
删除后:
POST请求到/_update端点来更新文档的特定字段。例如,POST /index_name/_update_by_query 允许你基于查询条件更新多个文档。_update_by_query操作详细说明:
原来没有age字段的内容也会被赋值
POST /xgss_test_index/_update_by_query
{
"script": {
"source": """
ctx._source.student.stream()
.filter(s -> s.name == params.name)
.forEach(s -> s.age = params.age);
""",
"lang": "painless",
"params": {
"name": "张三",
"age": 15
}
},
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "student",
"query": {
"term": {
"student.name": "张三"
}
}
}
}
}原来这个文档内容为:
{
"_index" : "xgss_test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "xE3m548Bc0MQKS2r84aV",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"student" : [
{
"name" : "王五",
"age" : 1
},
{
"name" : "马六",
"age" : 1
}
]
}
}执行以下命令:
POST /xgss_test_index/_update_by_query
{
"script": {
"source": """
ctx._source.student.removeIf(s -> s.name.equals(params.name));
""",
"lang": "painless",
"params": {
"name": "王五"
}
},
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "student",
"query": {
"term": {
"student.name": "王五"
}
}
}
}
}执行以后变为了如下,只删除了student中的一个成员
{
"_index" : "xgss_test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "xE3m548Bc0MQKS2r84aV",
"_score" : 1.0,
"_source" : {
"student" : [
{
"name" : "马六",
"age" : 1
}
]
}
}如果要先判断是否为空在进行删除
{
"script": {
"source": """
if (ctx._source.student != null) {
ctx._source.student.removeIf(s -> s.name != null && s.name.equals(params.name));
}
""",
"lang": "painless",
"params": {
"name": "王五"
}
},
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "student",
"query": {
"term": {
"student.name": "王五"
}
}
}
}
}DELETE /index_name/_doc/document_id:根据文档ID删除文档。
GET /index_name/_doc/document_id:根据文档ID检索文档。GET /index_name/_search:执行搜索查询并返回匹配的文档。你可以在请求体中定义查询条件。GET /myindex/_doc/myid也可以再query中查
GET /myindex/_search
{
"size": 100,
"query": {
"term": {
"_id": "123456"
}
}
}{
"from": 10,
"size": 10,
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
} 通过在URL末尾添加?pretty,你可以让Elasticsearch以更容易阅读的格式返回JSON响应。这将包括适当的缩进和换行符,使得JSON结构更加清晰。
你可以使用query结合_source字段的过滤功能来实现。_source字段允许你控制哪些字段应该被包含在返回的文档结果中。
{
"query": {
"term": { // 或者使用其他查询类型,如match, match_phrase等
"field1": "value1" // 替换为你的查询条件和值
}
},
"_source": ["field1", "field2"], // 只返回field1和field2字段
"stored_fields": ["field1", "field2"] // 如果字段被存储了,可以使用stored_fields代替_source
}
_source字段被设置为一个数组,包含了你想要返回的字段名称。这样,Elasticsearch将只返回这些字段的值,而不会返回整个文档。
注意,_source字段用于控制源JSON文档中的哪些字段应该被返回。如果字段是被存储的(即它们被映射为store: true),你也可以使用stored_fields参数来指定返回的字段。但是,通常建议仅使用_source,除非有特定的原因需要存储字段。
GET your_index_name/_search
{
"_source": {
"excludes": ["field1", "field2"]
},
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"lt": 10
}
}
}
}GET /your_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"range": {
"age": {
"lt": 6
}
}
}
]
}
}
}size指定为0
{
"size": 0, // 设置size为0以不包含文档在响应中
"aggs": {
"unique_field_values": {
"terms": {
"field": "your_field.keyword", // 注意要使用.keyword后缀(如果字段是文本类型并且被索引为keyword)
"size": 100 // 返回前100个唯一值,你可以根据需要调整这个值
}
}
}
} 使用term查询直接获取数量
GET /your_index/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"name": "张三"
}
},
"size": 0
}在返回的响应中,查看hits.total.value字段,它将给出匹配查询的文档数量。这种方式受到index.max_result_window参数的值影响,默认是10000.
可以再查询条件上添加track_total_hits=true来查询所有的,默认情况下,当Elasticsearch返回搜索结果时,它不会返回实际的总命中数,而是返回一个近似值(当结果集很大时)。这是因为在处理大量数据时,计算确切的总命中数可能会消耗大量资源。为了提高性能,Elasticsearch返回了一个近似值,该值通常足够接近实际值,以用于大多数用例。在某些情况下,你可能需要确切的总命中数。例如,当你需要知道查询结果的确切数量以便进行分页时,或者当你需要基于总命中数进行某些决策时。在这些情况下,你可以将track_total_hits参数设置为true来告诉Elasticsearch计算并返回确切的总命中数。
使用aggs查询
GET /xgss_test_index/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"students": {
"nested": {
"path": "student"
},
"aggs": {
"filtered_students": {
"filter": {
"match": {
"student.name": "张三"
}
}
}
}
}
}
} 返回:
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : null,
"hits" : [ ]
},
"aggregations" : {
"students" : {
"doc_count" : 2,
"filtered_students" : {
"doc_count" : 2
}
}
}
}注意这里的student是nested类型的,这里其实就存了一个文档,stdunt中存了两个name为张三的这里结果返回的是2.所以这里查询到的实际还是匹配的元素数量,不是文档的数量
使用value_count聚合
GET /your_index/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"count_by_name": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"name": "张三"
}
},
"aggs": {
"name_count": {
"value_count": {
"field": "_id" // 或者你可以使用任何总是存在的字段,如_id
}
}
}
}
}
}在返回的响应中,查看查看aggregations.count_by_name.doc_count来获取name为"张三"的文档数量。aggs进行的查询不受index.max_result_window参数的值影响
value_count查询说明:
value_count用于计算某个字段值的数量,用于统计某个值出现的次数.
比如这个:
GET /xgss_test_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"nested": {
"path": "student",
"query": {
"term": {
"student.name": {
"value": "张三"
}
}
}
}
}
]
}
},
"aggregations": {
"students_named_zhangsan": {
"nested": {
"path": "student"
},
"aggregations": {
"students_with_name": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"student.name": "张三"
}
},
"aggregations": {
"count_students": {
"value_count": {
"field": "_index"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}这个索引中student数组中存了两个name为张三的元素,最后查询出来是两条
{
"took" : 0,
"timed_out" : false,
"_shards" : {
"total" : 1,
"successful" : 1,
"skipped" : 0,
"failed" : 0
},
"hits" : {
"total" : {
"value" : 1,
"relation" : "eq"
},
"max_score" : 0.18232156,
"hits" : [
{
"_index" : "xgss_test_index",
"_type" : "_doc",
"_id" : "1",
"_score" : 0.18232156,
"_source" : {
"student" : [
{
"name" : "张三"
},
{
"name" : "张三"
}
]
}
}
]
},
"aggregations" : {
"students_named_zhangsan" : {
"doc_count" : 2,
"students_with_name" : {
"doc_count" : 2,
"count_students" : {
"value" : 2
}
}
}
}
}GET /your_index/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "student",
"query": {
"term": {
"student.name": "张三"
}
}
}
},
"aggs": {
"students_named_zhangsan": {
"nested": {
"path": "student"
},
"aggs": {
"count_students": {
"filter": {
"term": {
"student.name": "张三"
}
},
"aggs": {
"count": {
"value_count": {
"field": "_id" // 或者使用其他始终存在的字段,但在这里使用_id即可
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}在query部分使用了一个nested查询来限制哪些文档应该被包括在聚合中。
在aggs部分,我们再次使用nested聚合来确保我们对每个student对象进行计数,而不仅仅是外部文档。在这个嵌套的聚合中,我们使用了一个filter聚合来筛选出name为"张三"的student对象,并使用value_count聚合来对这些筛选后的对象进行计数。
查看返回的响应中的aggregations.students_named_zhangsan.count_students.count.value字段,你将得到name为"张三"的student对象的数量。
GET students_index/_search
{
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "student", // 指定nested类型的字段路径
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [ // 必须同时满足下面两个条件
{ "match": { "student.name": "张三" } }, // name为张三
{ "match": { "student.age": 15 } } // age为15
]
}
}
}
}
}对于只符合一个条件的文档不在返回值中
(1)直接用nested查询嵌套bool的must_not会直接先查找出有student值的文档,再过滤掉所有student成员的age属性符合must_not条件的文档
POST /xgss_test_index/_search
{
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "student",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"term": {
"student.age": {
"value": "15"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
}查询到的都有student对象,
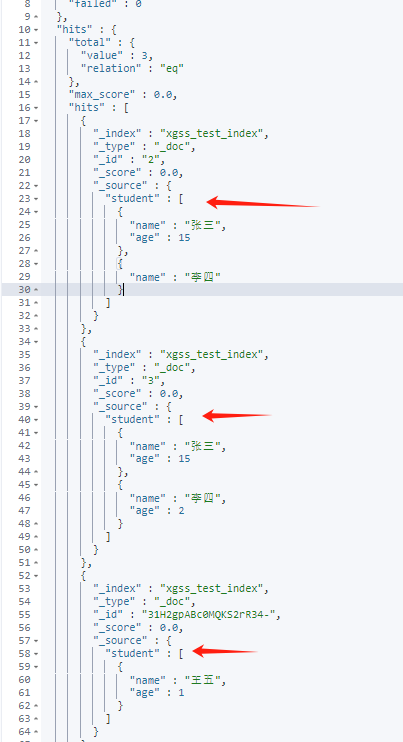
过滤掉了这个文档:

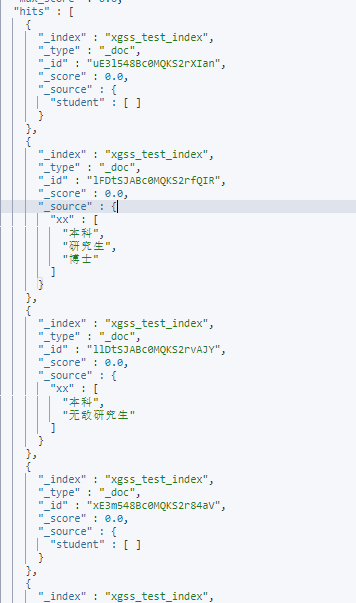
(2)如果外面bool的must_not查询嵌套nested类型的bool查询的must,查询原理是先执行外面的bool查询到服务条件文档,将student嵌套文档中任何元素服务must_nott条件的文档给过滤掉
如:查询语句
POST /xgss_test_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"nested": {
"path": "student",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"student.age": {
"value": "15"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
}查询结果:没有student属性的文档也会返回,任何有符合student.age为15的文档都会被过滤掉
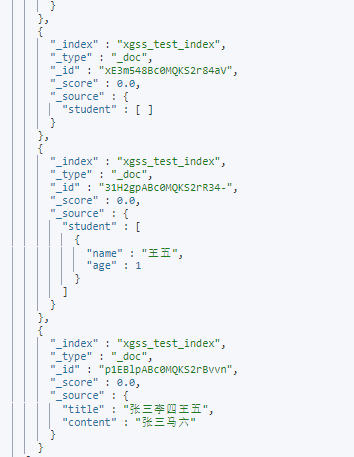
总结:本来是想过滤掉嵌套文档中age为15的文档,结果还是被查询到了
(3)如果是外面bool的must嵌套nested的must_not;这个效果跟(1)是一样的效果,只查询到有studen.age字段,且有值符合must_not条件的文档信息
POST /xgss_test_index/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"nested": {
"path": "student",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"term": {
"student.age": {
"value": "15"
}
}
}
]
}
}
}
}
]
}
}
} 
inner_hits可以在查询结果中显示嵌套文档中的符合查询条件的成员信息。
比如上面的must_not查询返回结果中student的成员中有age为15的也有age不是15的,我们加上innder_hits条件
POST /xgss_test_index/_search
{
"query": {
"nested": {
"path": "student",
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": [
{
"term": {
"student.age": {
"value": "15"
}
}
}
]
}
},"inner_hits": {}
}
}
}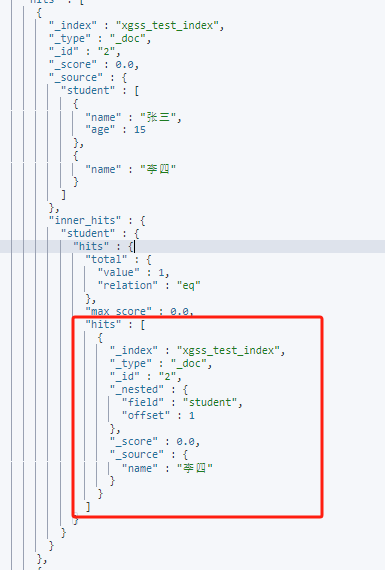


可以看到结果中把符合条件的student成员放到了inner_hits的返回结果中
inner_hits还可以设置部分属性:
size:控制返回的内部命中数量。
highlight:启用高亮显示匹配的文本。
explain:返回每个内部命中的评分细节。
_source:控制返回的内部命中文档的源字段。
如:
"inner_hits":{"size":3,"explain":false,"_source":{"includes":["student.name","student.age"],"excludes":[]}}
类似distinct
GET /your_index/_search
{
"size": 0,
"aggs": {
"unique_names": {
"terms": {
"field": "name.keyword",
"size": 1000 // 你可以根据需要调整这个值,以获取更多的不同值
}
}
}
}
match_all查询所有,也就是查询所有,默认查询10条,可以通过设置from和size指定查询哪些数据
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}代表完全匹配,即不进行分词器分析,文档中必须包含整个搜索的词汇
{
"query": {
"term": {
"schoolId": "2811000226000000678"
}
}
}多词语查询,查找符合词语列表的数据。如果要查询的字段索引为not_analyzed类型,则terms查询非常类似于关系型数据库中的in查询。
{
"query": {
"terms": {
"studentNo": [
"1",
"3"
]
}
}
}如果要做类似mysql中的not in查询,使用bool查询配合must not进行
如:对于nested类型
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": {
"nested": {
"path": "student_name", // student_name是nested字段的路径
"query": {
"terms": {
"student_name.keyword": ["张三", "李四"]
}
}
}
}
}
}
}对于普通的类型
GET myindex/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must_not": {
"terms": {
"student_name.keyword": ["张三", "李四"]
}
}
}
}
}Bool(布尔)查询是一种复合型查询,它可以结合多个其他的查询条件。主要有3类逻辑查询:
must:查询结果必须符合该查询条件(列表)。
should:类似于in的查询条件。如果bool查询中不包含must查询,那么should默认表示必须符合查询列表中的一个或多个查询条件。
must_not:查询结果必须不符合查询条件(列表)。
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"classNo": "2"
}
},
{
"term": {
"isLeader": "true"
}
}
]
}
}
}ids查询:
通过指定一个ID列表来检索多个文档,想要检索ID为1、3和5的文档。
{
"query": {
"ids": {
"values": ["1", "3", "5"]
}
}
}Prefix Query前缀查询:
{
"query": {
"prefix": {
"name": "赵"
}
}
}range query:
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": "18", // 表示>=
"lte": "20" // 表示<=
}
}
}
}Wildcard Query通配符查询:
通配符查询,是简化的正则表达式查询,包括下面两类通配符:
* 代表任意(包括0个)多个字符
? 代表任意一个字符
查找名字的最后一个字是“亮”的同学,查询结果是学号为5的诸葛亮。
{
"query": {
"wildcard": {
"name": "*亮"
}
}
}Regexp Query 正则表达式查询
{
"query": {
"regexp": {
"address": ".*长沙市.*" // 这里的.号表示任意一个字符
}
}
}match查询:
用于全文搜索,Match查询默认会考虑字段的分析器设置。这意味着如果字段在索引时被配置了一个特定的分析器,那么查询时也会使用相同的分析器来处理查询字符串。它默认使用OR逻辑,即只要文档包含查询中的一个或多个分词,就会被视为匹配。不考虑这些单词的顺序或位置。
GET /products/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"description": "智能手机"
}
}
}
//operator指定多个词条之间的匹配逻辑"AND"表示所有词条都必须匹配,"OR"表示至少有一个词条匹配即可。默认值是"OR"。
{
"query": {
"match": {
"description": {
"query": "智能手机 快充",
"operator": "AND"
}
}
}
}
//fuzziness:这个参数用于模糊匹配,可以指定一个编辑距离来允许查询中的词与文档中的词有一定的差异。
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": {
"query": "iphne",
"fuzziness": 2
}
}
}
}
//prefix_length:这个参数用于模糊匹配时,指定从词的前多少个字符开始不允许被模糊。默认值是0,表示从词的开始就可以进行模糊匹配。
{
"query": {
"match": {
"brand": {
"query": "appl",
"fuzziness": 2,
"prefix_length": 2 //从“appl”的前两个字符“ap”开始不允许被模糊,所以只会匹配到像“apple”这样的词。
}
}
}
}
//minimum_should_match:这个参数用于指定文档中至少包含多少个关键词才算匹配成功。它可以帮助控制返回的文档与查询的相关度。
{
"query": {
"match": {
"features": {
"query": "防水 防尘 抗震",
"minimum_should_match": "2<3" //这个查询会返回features字段中至少包含“防水”、“防尘”和“抗震”这三个词中的两个词的文档。
}
}
}
}
//zero_terms_query:当查询语句被分析后没有剩余词条时,这个参数用来控制查询的行为。默认是"NONE",表示不返回任何文档;也可以设置为"ALL",表示返回所有文档。
//Match查询还提供了其他一些参数,如analyzer(用于指定分析器)、lenient(控制查询对格式错误的容忍度)等。Match_phrase 查询:
它要求分词在文档中的顺序必须与查询中的顺序相同,并且通常要求这些分词是相邻的。
我们想要搜索标题中精确包含“Elasticsearch 搜索”这个短语的文档,我们应该使用match_phrase查询。
{
"query": {
"match_phrase": {
"title": "Elasticsearch 搜索"
}
}
}Elasticsearch会查找标题字段中精确包含“Elasticsearch”后面紧跟着“搜索”这两个词的文档。如果这两个词在文档中是分开的,或者它们的顺序与查询中的不同,那么该文档将不会被匹配。
filter查询方式都可以通过设置_cache为true来缓存数据。如果下一次恰好以相同的查询条件进行查询并且该缓存没有过期,就可以直接从缓存中读取数据。缓存的清理:缓存信息不够用时会按照最近最少用的先清理原则。
filter不支持Wildcard查询(通配符查询)。
term查询:
{
"filter": {
"term": {
"name": "诸葛亮",
"_cache" : true // 与query主要是这里的区别,可以设置数据缓存
}
}
}bool查询:
{
"filter": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{
"term": {
"classNo": "2"
}
},
{
"term": {
"isLeader": "true"
}
}
]
}
}
}exists查询
存在查询,查询指定字段至少包含一个非null值的数据。如果字段索引为not_analyzed类型,则查询sql中的is not null查询方式。
在query范围内不支持使用exists,必须放在filter的下面
{
"filter": {
"exists": {
"field": "address"
}
}
}Missing查询
缺失值查询,与Exists查询正好相反。该查询也是必须放在filter里面。
查询地址不存在的学生
{
"filter": {
"missing": {
"field": "address"
}
}
}Prefix查询(前缀查询)
{
"filter": {
"prefix": {
"name": "赵"
}
}
}range查询
{
"filter": {
"range": {
"age": {
"gte": "18",
"lte": "20"
}
}
}
}terms查询
多词语查询,查找符合词语列表的数据。如果要查询的字段索引为not_analyzed类型,则terms查询非常类似于关系型数据库中的in查询
{
"filter": {
"terms": {
"studentNo": [
"1",
"3"
]
}
}
}Regexp查询(正则表达式查询)
{
"filter": {
"regexp": {
"address": ".*长沙市.*"
}
}
}在Elasticsearch 7.x及更高版本中,建议使用bool查询结合filter子句,因为filter子句在更早期的版本中是一个顶层的查询参数,而在后续版本中它通常被放置在bool查询内部。
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "match": { "title": "Search" }},
{ "match": { "content": "Elasticsearch" }}
],
"filter": [
{ "term": { "status": "published" }},
{ "range": { "publish_date": { "gte": "2015-01-01" }}}
]
}
}
}query 参数表示整个语句是处于 query context 中
bool 和 match 语句被用在 query context 中,也就是说它们会计算每个文档的匹配度(_score)
filter 参数则表示这个子查询处于 filter context 中
filter 语句中的 term 和 range 语句用在 filter context 中,它们只起到过滤的作用,并不会计算文档的得分。
es5.3后支持collapse,
GET /xgss_test_index/_search
{
"query": {
"term": {
"abcd": "456"
}
},"collapse": {
"field": "abcd"
}
}结果返回的total跟没有加collapse是一样的,就是返回的记录中name值重复的不会返回
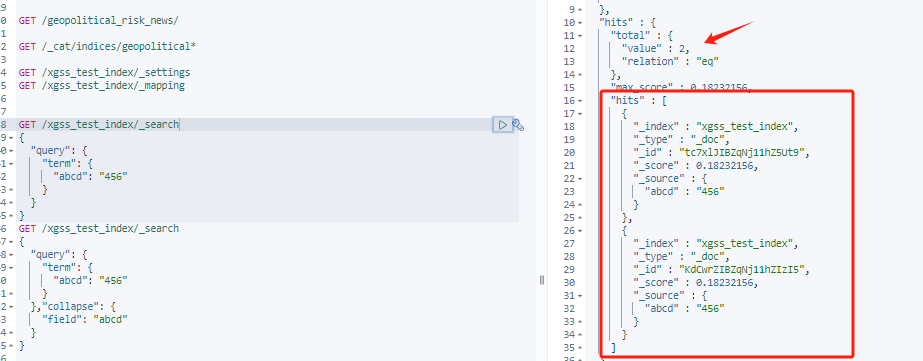
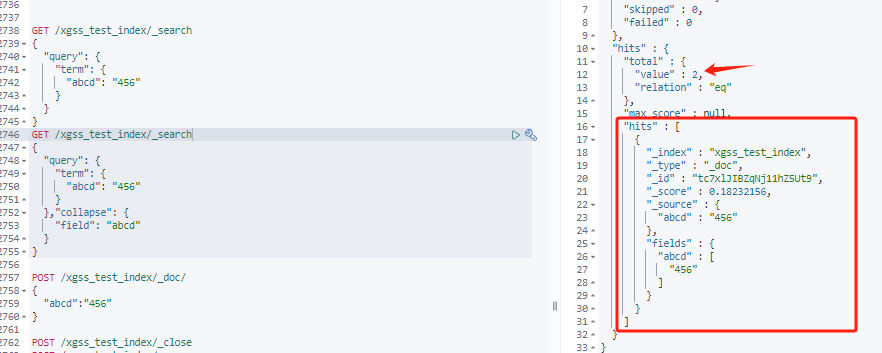
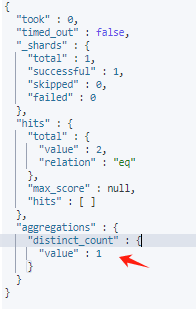
查询去重后的总数量
在_count查询中不能使用collapse参数,计算总数量需要用到aggs+cardinality进行查询
GET /xgss_test_index/_search
{
"size": 0,
"query": {
"term": {
"abcd": "456"
}
},"aggs": {
"distinct_count": {
"cardinality": {
"field": "abcd"
}
}
}
}
语法:
GET /<index_name>/_search
{
"size": 0, // 设置返回的文档数量为0,因为我们通常只对聚合结果感兴趣
"query": {
// ... 查询条件 ...
},
"aggs": {
"<aggregation_name>": {
"<aggregation_type>": {
// ... 聚合参数 ...
},
"aggs": {
// ... 子聚合 ...
}
}
}
}聚合类型:
Terms 聚合
按字段的值进行分组。类似mysql的distinct和group
"aggs": {
"groups": {
"terms": {
"field": "<field_name>",
"size": 10, // 返回的桶的最大数量
"order": { // 排序桶
"_key": "asc"
},
"include": "<value>", // 包含特定的桶
"exclude": "<value>", // 排除特定的桶
"min_doc_count": 1, // 桶中文档的最小数量
"shard_size": 200, // 每个分片返回的桶的最大数量
"show_term_doc_count_error": false // 是否显示文档计数的近似误差
}
}
}GET /sales/_search
{
"size": 0, // 不返回文档,只返回聚合结果
"aggs": {
"products": { // 聚合的名称
"terms": { // 使用terms聚合按字段分组
"field": "product_id"
},
"aggs": {
"total_sales": { // 内部聚合的名称
"sum": { // 使用sum聚合计算销售额的总和
"field": "sales_amount"
}
}
}
}
}
}Filters 聚合
根据多个过滤条件定义桶。
"aggs": {
"filters": {
"filters": {
"<filter_name>": { "match": { "<field_name>": "<value>" } },
// ... 其他过滤条件 ...
}
}
}Range 聚合
对数值字段进行范围分组。
"aggs": {
"prices": {
"range": {
"field": "<numeric_field>",
"ranges": [
{ "from": 0, "to": 100 },
{ "from": 100, "to": 200 }
// ... 其他范围 ...
]
}
}
}Metrics 聚合
用于计算数值字段的统计信息,如平均值、总和、最大值、最小值等。
"aggs": {
"average_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "<numeric_field>"
}
},
"total_sales": {
"sum": {
"field": "<numeric_field>"
}
}
// ... 其他metrics聚合 ...
}子聚合
你可以在聚合内部嵌套其他聚合,称为子聚合,以便对分组后的数据进行进一步的分析。
"aggs": {
"products": {
"terms": {
"field": "product_id"
},
"aggs": {
"average_price": {
"avg": {
"field": "price"
}
}
// ... 其他子聚合 ...
}
}
}POST my_index/_analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "how are you"
}
span_near可以进行嵌套
GET test_span/_search
{
"query": {
"span_near": {
"clauses": [
{
"span_near": {
"clauses": [
{
"span_term": {
"content": {
"value": "war"
}
}
},
{
"span_term": {
"content": {
"value": "uav"
}
}
}
],
"slop": 0,
"in_order": true
}
},
{
"span_near": {
"clauses": [
{
"span_term": {
"content": {
"value": "uav"
}
}
},
{
"span_term": {
"content": {
"value": "drone"
}
}
}
],
"slop": 0,
"in_order": true
}
}
],
"slop": 1,
"in_order": true
}
}
}