再玩亿关小游戏
444.26MB · 2025-11-02
java原生HttpURLConnection
第三方的开源框架HTTPClient
org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
httpclient是实现发送http请求的一种开源框架
在HTTP协议中定义的请求报文的第一行必须包含:请求方法, 请求URI ,HTTP协议版本。
HttpClient 支持所有定义在HTTP/1.1中的请求方法的拆箱工作: GET, HEAD, POST, PUT,DELETE,TRACE OPTIONS. 分别对应的类是:HttpGet,HttpHead, HttpPost,HttpPut, HttpDelete,HttpTrace, HttpOptions。
URI是一个统一资源定位符用来标识想要从哪获取资源. HTTP request URIs包含:protocol scheme(http://*,https*:*//),host name ,port, resource path, 可选的query,可选的fragment
HttpGet httpget = new HttpGet("http://www.*g*oo*gle.com/search?hl=en&q=httpclient&btnG=Google+Search&aq=f&oq=");
HttpClient 提供了 URIBuilder工具类来简化request URIs的创建和修改.
|
//uri就是JDK中默认的java.net.URI。可以想象为在浏览器中输入网址的过程 java.net.URI uri=new URIBuilder().setScheme("http") .setHost("www.baidu.com") .setPath("/search") .setParameter("q", "httpclient") .setParameter("btnG", "Google Search") .setParameter("aq", "f") .setParameter("oq", "") .build();//可以想象为用什么方法去访问服务,就像表单提交时候选择Get还是Post HttpGet httpget=new HttpGet(uri);//在get请求实体中同样可以拆箱获取uri httpget.getURI(); |
TTP response 是在服务器在已经接收和处理请求消息之后返回给客户端的信息. 消息中一
定包含了:protocol version ,数值型的status code,状态解释短语textual phrase。
|
//在服务器中 HttpResponse response=new BasicHttpResponse(org.apache.http.HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1,org.apache.http.HttpStatus.SC_OK, "OK");//同样可以进行拆箱的工作获取相关参数System.out.println(response.getProtocolVersion());//StatusLine 其实就是响应中的第一行,包含协议版本号,状态,短语System.out.println(response.getStatusLine().toString()); System.out.println(response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode()); System.out.println(response.getStatusLine().getReasonPhrase()); |
一个HTTP报文可能包含很多个header来表述报文的属性例如: content length, content type等等. HttpClient提供了对http报文head进行查询、添加、移除、枚举的方法。
|
//在服务器中 HttpResponse response=new BasicHttpResponse(org.apache.http.HttpVersion.HTTP_1_1,org.apache.http.HttpStatus.SC_OK, "OK"); response.addHeader("Set-Cookie","c1=a; path=/; domain=localhost"); response.addHeader("Set-Cookie", "c2=b; path="/", c3=c; domain="localhost"");//同样可以进行拆箱的工作,获取Header Header h1 = response.getFirstHeader("Set-Cookie"); System.out.println(h1); Header h2 = response.getLastHeader("Set-Cookie"); System.out.println(h2); Header[] hs = response.getHeaders("Set-Cookie"); System.out.println(hs.length);
|
最高效的获取所有header的方法是使用 HeaderIterator接口。
|
//相当于只是取到了header HeaderIterator it = response.headerIterator("Set-Cookie"); while (it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); }
|
当然也提供了非常方便的解析header elements部分报文的方法。
|
HeaderElementIterator hei=new BasicHeaderElementIterator(response.headerIterator("Set-Cookie")); while (it.hasNext()) { HeaderElement elem = hei.nextElement(); System.out.println(elem.getName() + " = " + elem.getValue()); //当然可以以键值对的形式读取 NameValuePair[] params = elem.getParameters(); for (int i = 0; i < params.length; i++) { System.out.println(" " + params[i]); } |
在HTTP request 和response报文中可以传输一个content entity. Entities是optional(比如:HttpHead方法就不会返回entity). Requests that use entities are referred to as entity enclosing requests(使用实体的请求被称为实体封装请求).在HTTP定义了两种 entity enclosing 请求方法: POST 和 PUT. 响应通常期望包含内容实体(content entity).此规则有例外情况,例如HEAD 方法和204 No Content,304 Not Modified, 205 Reset Content 响应。
HttpClient 依据content的来源将entity分为三种:(官网中的分类确实让人不知所云。)
streamed: 内容是从流中接收到的,或者是即时生成的(generated on the fly)。特别地,该类别包括从HTTP响应接收到的实体. Streamed entities 通常不可重复
self-contained: 内容在内存中或通过独立于连接或其他实体的方式获取。Self-contained entities 通常是可重复的. 这是HTTP requests最常用的entities
wrapping: 通常 content 来自于另一个entity。
当从HTTP响应(streaming out content)流出内容时,此区别对于连接管理(connection management)很重要.使用HttpClient仅当sent的时候request entities才会由应用创建,streamed 和 self-contained 的差异不是很重要.在这种情况下,建议将不可重复的实体视为streamed,将可重复的实体视为self-contained。
一个entity可以重复也就意味着它的content可以被多次读取. self contained entities (ByteArrayEntity、StringEntity)。
因为一个entity可以使用二进制和字符两种形式表示, 所以entity支持字符encodings (用以支持latter, ie. character content)。
当执行带有enclosed content的request请求(post、put)或者当请求成功返回响应体时entity会被创建。
从 entity读取content, 既可以使用 HttpEntity#getContent()方法, 将返回java.io.InputStream, 也可以向HttpEntity#writeTo(OutputStream)方法提供输出流,一旦所有内容都已写入给定流,该方法将返回。
entity的 HttpEntity#getContentType()和 HttpEntity#getContentLength()方法对应的参数是header中:Content-Type 和Content-Length headers (如果可访问的话).因为在HttpEntity#getContentEncoding()可以获取Content-Type header 含mime-types :text/plain 、 text/html. 如果header不可访问则Content-Length返回-1 ,Content-Type返回NULL .如果Content-Type header 可以访问则会返回Header对象.
当为outgoing message外发消息创建实体时,该元数据必须由实体的创建者提供。
|
StringEntity entity=new StringEntity("important message",ContentType.create("text/plain","utf-8")); //Entity中可以包含的信息Content-Type entity.getContentType(); //Content-Length entity.getContentLength(); //支持的编码:Content-Encoding;Content-Type: text/plain; charset=utf-8 entity.getContentEncoding(); //显示entity的content :important message EntityUtils.toString(entity); //将entity转化为Byte字节数组 EntityUtils.toByteArray(entity);
|
确保释放低级别资源
为了保证能正确释放系统资源,必须关闭与实体或响应本身相关联的内容流。
|
//将其想象成建一个浏览器的过程,HttpClients我个人感觉可以类比Collection和Collections的关系,提供HTTPClient的工具 CloseableHttpClient httpclient=HttpClients.createDefault();//可以想象为用什么方法去访问服务,就像表单提交时候选择Get还是Post HttpGet httpget=new HttpGet("www.baidu.com");//可以想象为点击鼠标的过程,或者是提交表单的过程。有返回值。。。。。 CloseableHttpResponse response=httpclient.execute(httpget);try { //业务处理层的东西 HttpEntity entity=response.getEntity(); if(entity!=null) { InputStream is=entity.getContent(); try { //dosomething }finally { //关闭entity的输入流 is.close(); } } }finally{ //关闭响应的流 response.close(); } |
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> <version>4.3.5</version> </dependency> |
DoGET.java
|
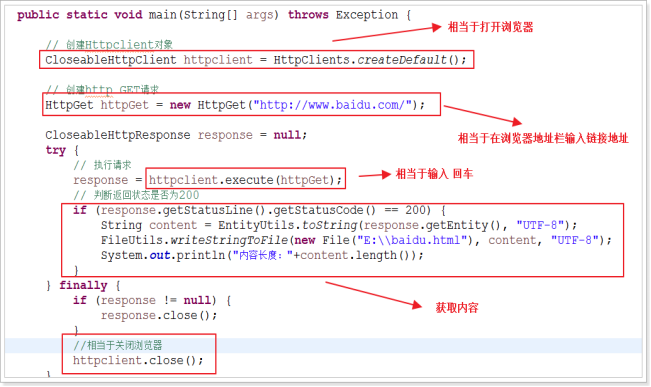
public class DoGET {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 创建Httpclient对象 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault();
// 创建http GET请求 HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet("http://www.bai***du.com/s?wd=java");
CloseableHttpResponse response = null; try { // 执行请求 response = httpclient.execute(httpGet); // 判断返回状态是否为200 if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"); FileUtils.writeStringToFile(new File("E:\baidu.html"), content, "UTF-8"); System.out.println("内容长度:"+content.length()); } } finally { if (response != null) { response.close(); } //相当于关闭浏览器 httpclient.close(); }
}
} |
|
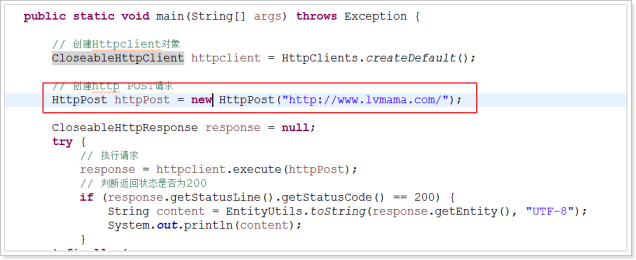
public class DoGETParam { public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { // 创建Httpclient对象 CloseableHttpClient httpclient = HttpClients.createDefault(); // 定义请求的参数 URI uri = new URIBuilder("http://www.b***aidu.com/s").setParameter("wd", "java").build(); System.out.println(uri); // 创建http GET请求 HttpGet httpGet = new HttpGet(uri); CloseableHttpResponse response = null; try { // 执行请求 response = httpclient.execute(httpGet); // 判断返回状态是否为200 if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { String content = EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"); System.out.println(content); } } finally { if (response != null) { response.close(); } httpclient.close(); } } } |
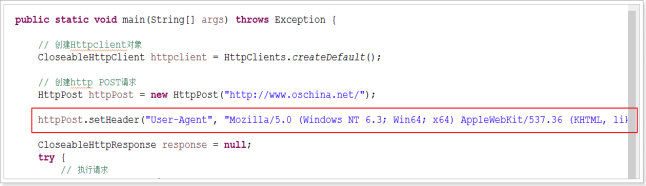
核心:设置请求头信息。
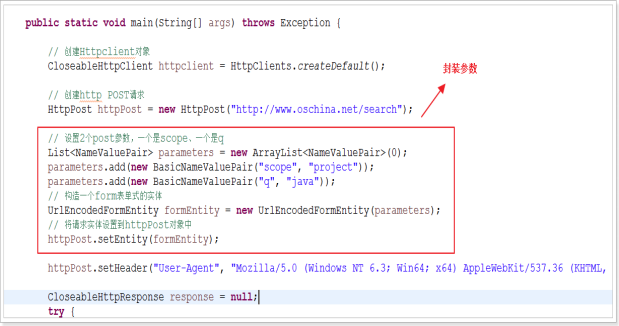
一、为什么要用Http连接池
1、降低延迟:如果不采用连接池,每次连接发起Http请求的时候都会重新建立TCP连接(经历3次握手),用完就会关闭连接(4次挥手),如果采用连接池则减少了这部分时间损耗,别小看这几次握手,本人经过测试发现,基本上3倍的时间延迟
2、支持更大的并发:如果不采用连接池,每次连接都会打开一个端口,在大并发的情况下系统的端口资源很快就会被用完,导致无法建立新的连接
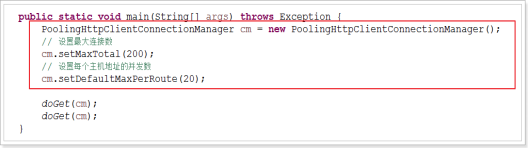
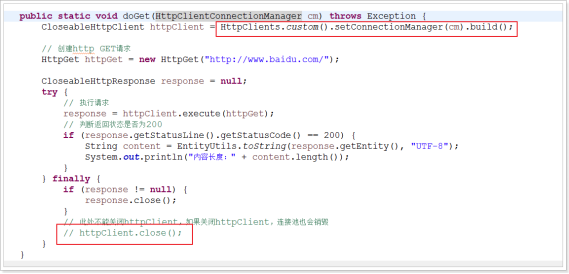
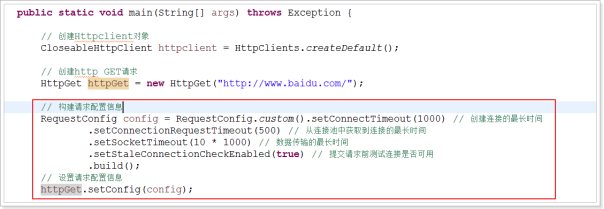
核心:使用一个单独的线程完成连接池中的无效链接的清理。
|
public static class IdleConnectionEvictor extends Thread { private final HttpClientConnectionManager connMgr; private volatile boolean shutdown; public IdleConnectionEvictor(HttpClientConnectionManager connMgr) { this.connMgr = connMgr; } @Override public void run() { try { while (!shutdown) { synchronized (this) { wait(5000); // 关闭失效的连接 connMgr.closeExpiredConnections(); } } } catch (InterruptedException ex) { // 结束 } }
public void shutdown() { shutdown = true; synchronized (this) { notifyAll(); } } }
|
将原有的Httpclient使用方法改写成Spring的配置即可。
注意:
Httpclient对象是多例还是单例?
|
<bean id="httpClientConnectionManager" class="org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager" destroy-method="shutdown"> <!-- 设置最大连接数 --> <property name="maxTotal" value="${http.maxTotal}"/> <!-- 设置每个主机地址的并发数 --> <property name="defaultMaxPerRoute" value="${http.defaultMaxPerRoute}"/> </bean>
<bean id="httpClientBuilder" class="org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClientBuilder"> <property name="connectionManager" ref="httpClientConnectionManager"/> </bean>
<!-- 通过httpClientBuilder得到httpClient对象,并且要设置httpClient为多利模式 --> <bean id="httpClient" class="org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient" factory-bean="httpClientBuilder" factory-method="build" scope="prototype"/>
<!-- 构造请求参数 --> <bean id="requestConfigBuilder" class="org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig.Builder"> <property name="connectTimeout" value="${http.connectTimeout}"/> <property name="connectionRequestTimeout" value="${http.connectionRequestTimeout}"/> <property name="socketTimeout" value="${http.socketTimeout}"/> <property name="staleConnectionCheckEnabled" value="${http.staleConnectionCheckEnabled}"/> </bean>
<bean id="requestConfig" class="org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig" factory-bean="requestConfigBuilder" factory-method="build"/>
<!-- 清理无效连接 --> <bean class="com.taotao.common.service.IdleConnectionEvictor" destroy-method="shutdown"> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="httpClientConnectionManager"/> </bean>
|
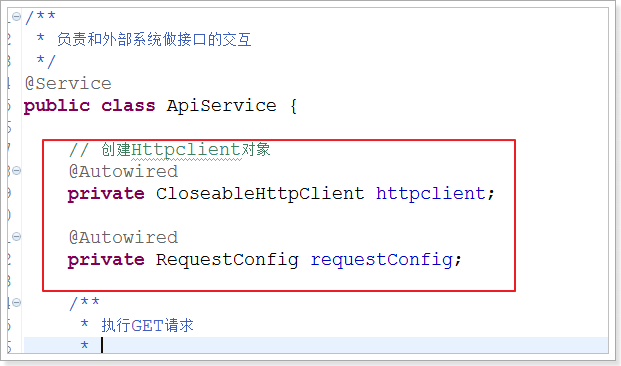
使用:
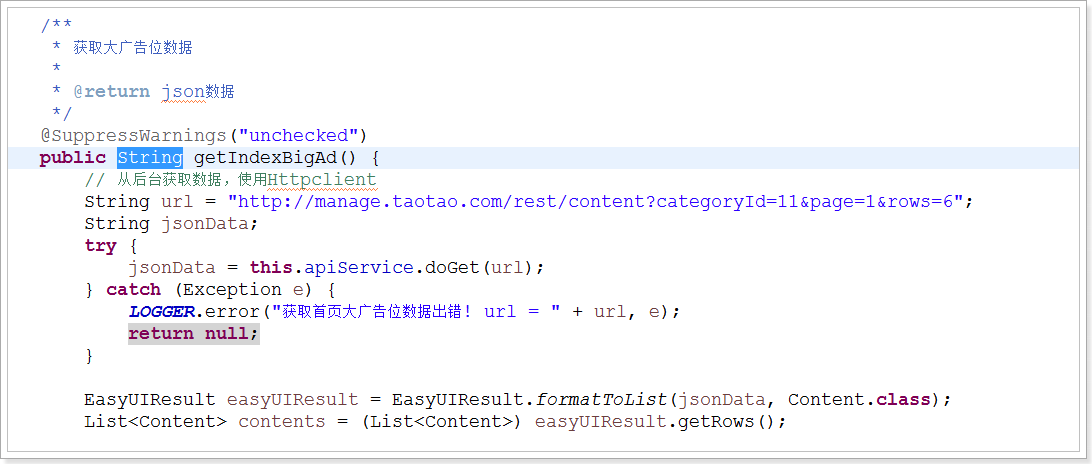
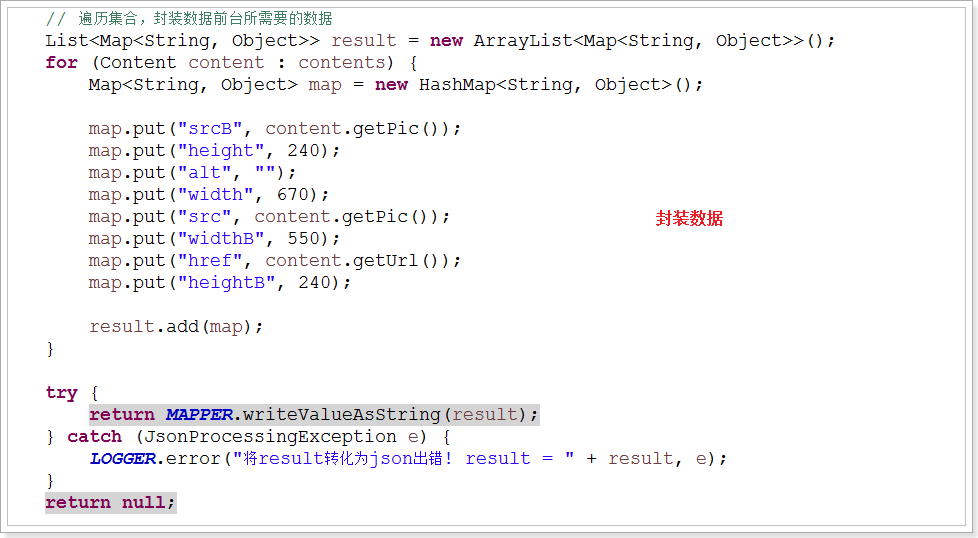
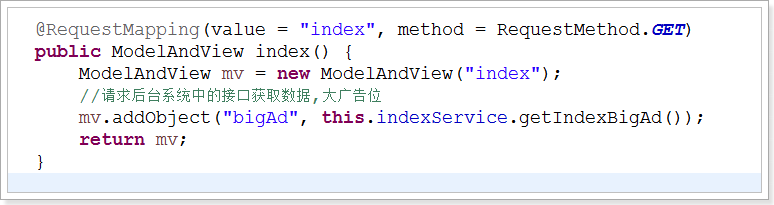
Jsp:
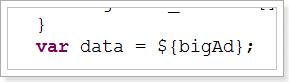
依赖
|
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.httpcomponents</groupId> <artifactId>httpclient</artifactId> <version>4.5.2</version> </dependency> |
建立配置文件
httpclient.properties
|
#设置最大连接数 http.maxTotal=200 #设置每个主机的并发数 http.defaultMaxPerRoute=20 #创建连接的最长时间 http.connectTimeout=1000 #从连接池中获取到连接的最长时间 http.connectionRequestTimeout=500 #数据传输的最长时间 http.socketTimeout=10000 #提交请求前测试连接是否可用 http.staleConnectionCheckEnabled=true |
新建http配置文件:applicationContext-httpclient.xml
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.*spring*fr*amework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.**w*3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:mvc="http://www.*spr*in*gframework.org/schema/mvc" xmlns:context="http://www.springf*ramew*o*rk.org/schema/context" xmlns:aop="http://www.sp*ringfram**ework.org/schema/aop" xmlns:tx="http://www.spri**ngfra*mework.org/schema/tx" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.*spring*fr*amework.org/schema/beans http://www.*spring*fr*amework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.2.xsd http://www.*spr*in*gframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.*spr*in*gframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-3.2.xsd http://www.springf*ramew*o*rk.org/schema/context http://www.springf*ramew*o*rk.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.2.xsd http://www.sp*ringfram**ework.org/schema/aop http://www.sp*ringfram**ework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-3.2.xsd http://www.spri**ngfra*mework.org/schema/tx http://www.spri**ngfra*mework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx-3.2.xsd ">
<!--创建httpclient的连接池 --> <bean id="httpClientConnectionManager" class="org.apache.http.impl.conn.PoolingHttpClientConnectionManager" destroy-method="shutdown"> <!-- 设置最大连接数 --> <property name="maxTotal" value="${http.maxTotal}" /> <!-- 设置每个主机的并发数 --> <property name="defaultMaxPerRoute" value="${http.defaultMaxPerRoute}" /> </bean>
<!-- 创建httpClient对象 --> <!-- httpClient是由HttpClientBuilder通过build方法创建,这个可以设置连接池 --> <!-- 1.创建HttpClientBuilder --> <bean id="httpClientBuilder" class="org.apache.http.impl.client.HttpClientBuilder"> <!--设置连接池 --> <property name="connectionManager" ref="httpClientConnectionManager"></property> </bean> <!-- 2.创建httpClient --> <!-- 通过httpClientBulider得到httpClient对象,并且设置httpClient为多利模式 --> <!-- 要保证httpClient为多利,以为每次都是新的http请求 --> <bean id="httpClient" class="org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient" factory-bean="httpClientBuilder" factory-method="build" scope="prototype" />
<!-- 构造请求参数 --> <bean id="requestConfigBuilder" class="org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig.Builder"> <!-- 创建连接的最长时间 --> <property name="connectTimeout" value="${http.connectTimeout}" /> <!-- 从连接池中获取到连接的最长时间 --> <property name="connectionRequestTimeout" value="${http.connectionRequestTimeout}" /> <!-- 数据传输的最长时间 --> <property name="socketTimeout" value="${http.socketTimeout}" /> <!-- 提交请求前测试连接是否可用 --> <property name="staleConnectionCheckEnabled" value="${http.staleConnectionCheckEnabled}" /> </bean> <bean id="requestConfig" class="org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig" factory-bean="requestConfigBuilder" factory-method="build" />
<!--清理无效的http连接 --> <bean class="com.xgss.common.IdleConnectionEvictor" destroy-method="shutdown"> <constructor-arg index="0" ref="httpClientConnectionManager"></constructor-arg> </bean> </beans> |
关闭无效链接的类IdleConnectionEvictor
|
package com.xgss.common;
import org.apache.http.conn.HttpClientConnectionManager;
public class IdleConnectionEvictor extends Thread {
private final HttpClientConnectionManager connMgr;
private volatile boolean shutdown;
public IdleConnectionEvictor(HttpClientConnectionManager connMgr) { this.connMgr = connMgr; }
@Override public void run() { try { while (!shutdown) { synchronized (this) { wait(5000); // 关闭失效的连接 connMgr.closeExpiredConnections(); } } } catch (InterruptedException ex) { // 结束 } }
public void shutdown() { shutdown = true; synchronized (this) { notifyAll(); } } }
|
http处理类
|
package com.xgss.service.impl;
import java.io.IOException; import java.net.URI; import java.net.URISyntaxException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map;
import org.apache.http.NameValuePair; import org.apache.http.client.ClientProtocolException; import org.apache.http.client.config.RequestConfig; import org.apache.http.client.entity.UrlEncodedFormEntity; import org.apache.http.client.methods.CloseableHttpResponse; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet; import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpPost; import org.apache.http.client.utils.URIBuilder; import org.apache.http.impl.client.CloseableHttpClient; import org.apache.http.message.BasicNameValuePair; import org.apache.http.util.EntityUtils; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.xgss.service.HttpService;
@Service public class HttpServiceImpl implements HttpService{
// 创建Httpclient对象 @Autowired(required = false) private CloseableHttpClient httpClient;
// 请求信息的配置 @Autowired(required = false) private RequestConfig requestConfig;
/** * 执行Get请求 * * @param url * @return 请求到的内容 * @throws URISyntaxException * @throws IOException * @throws ClientProtocolException */ public String doGet(String url) throws URISyntaxException, ClientProtocolException, IOException { return doGet(url, null); }
/** * 执行Get请求 * * @param url * @param params * 请求中的参数 * @return 请求到的内容 * @throws URISyntaxException * @throws IOException * @throws ClientProtocolException */ public String doGet(String url, Map<String, Object> params) throws URISyntaxException, ClientProtocolException, IOException { // 定义请求的参数 URI uri = null; if (params != null) { URIBuilder builder = new URIBuilder(url); for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : params.entrySet()) { builder.addParameter(entry.getKey(), String.valueOf(entry.getValue())); } uri = builder.build(); }
// 创建http GET请求 HttpGet httpGet = null; if (uri != null) { httpGet = new HttpGet(uri); } else { httpGet = new HttpGet(url); } // 设置请求参数 httpGet.setConfig(this.requestConfig);
// 请求的结果 CloseableHttpResponse response = null; try { // 执行请求 response = httpClient.execute(httpGet); // 判断返回状态是否为200 if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { // 获取服务端返回的数据,并返回 return EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"); } } finally { if (response != null) { response.close(); } } return null; }
/** * * @param url * @param params * 请求中的参数 * @return 请求到的内容 * @throws URISyntaxException * @throws ClientProtocolException * @throws IOException */ public String doPost(String url, Map<String, Object> params) throws URISyntaxException, ClientProtocolException, IOException { // 设置post参数 List<NameValuePair> parameters = null; // 构造一个form表单式的实体 UrlEncodedFormEntity formEntity = null;
// 定义请求的参数 if (params != null) { // 设置post参数 parameters = new ArrayList<NameValuePair>(); for (Map.Entry<String, Object> entry : params.entrySet()) { // 添加参数 parameters.add(new BasicNameValuePair(entry.getKey(), String .valueOf(entry.getValue()))); } // 构造一个form表单式的实体 formEntity = new UrlEncodedFormEntity(parameters); }
// 创建http GET请求 HttpPost httpPost = null; if (formEntity != null) { httpPost = new HttpPost(url); // 将请求实体设置到httpPost对象中 httpPost.setEntity(formEntity); // 伪装浏览器请求 httpPost.setHeader( "User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2272.118 Safari/537.36"); } else { httpPost = new HttpPost(url); // 伪装浏览器请求 httpPost.setHeader( "User-Agent", "Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 6.3; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/41.0.2272.118 Safari/537.36"); } // 设置请求参数 httpPost.setConfig(this.requestConfig);
// 请求的结果 CloseableHttpResponse response = null; try { // 执行请求 response = httpClient.execute(httpPost); // 判断返回状态是否为200 if (response.getStatusLine().getStatusCode() == 200) { // 获取服务端返回的数据,并返回 return EntityUtils.toString(response.getEntity(), "UTF-8"); } } finally { if (response != null) { response.close(); } } return null; }
/** * * @param url * @param params * 请求中的参数 * @return 请求到的内容 * @throws URISyntaxException * @throws ClientProtocolException * @throws IOException */ public String doPost(String url) throws URISyntaxException, ClientProtocolException, IOException { return doPost(url, null); } } |
测试使用
|
package com.xgss.web;
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.xgss.service.HttpService;
@Controller public class HttpclientTestController{ @Autowired HttpService httpService;
@ResponseBody @RequestMapping("httpclientTest") public Map<String,String> httpclientTest(String[] args) { String url="http://test.fi***fedu.com/kyxl-web/teacher/task/yearclass"; Map<String,String> map =new HashMap<String,String>(); try { // Map<String, Object> maps = new HashMap<String, Object>(); // maps.put("wd", "java"); // String string = httpService.doPost( url, maps); String doGetData = httpService.doGet(url); String doPostData = httpService.doPost(url); map.put("doGetData:", doGetData); map.put("doPostData:", doPostData);
} catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } return map; } }
|
connect timed out:
是HttpClient发送请求的地方开始到连接上目标url主机地址的时间
理论上是距离越短越快,线路越通畅越快,但是由于路由复杂交错,往往连接上的时间都不固定
Read timed out
是HttpClient已经连接到了目标服务器,然后进行请求处理的时间
对于404是域名可以访问到,但具体的请求的地址没有找到
响应码分五种类型,由它们的第一位数字表示:
1xx:信息,请求收到,继续处理
2xx:成功,行为被成功地接受、理解和采纳
3xx:重定向,为了完成请求,必须进一步执行的动作
4xx:客户端错误,请求包含语法错误或者请求无法实现
5xx:服务器错误,服务器不能实现一种明显无效的请求
|
状态码 |
说明 |
详情 |
|
100 |
继续 |
请求者应当继续提出请求。服务器已收到请求的一部分,正在等待其余部分 |
|
101 |
切换协议 |
请求者已要求服务器切换协议,服务器已确认并准备切换 |
|
200 |
成功 |
服务器已成功处理了请求 |
|
202 |
已接受 |
服务器已接受请求,但尚未处理 |
|
203 |
非授权信息 |
服务器已成功处理了请求,但返回的信息可能来自另一个源 |
|
204 |
无内容 |
服务器成功处理了请求,但没有返回任何内容 |
|
205 |
重置内容 |
服务器成功处理了请求,内容被重置 |
|
206 |
部分内容 |
服务器成功处理了部分请求 |
|
300 |
多种选择 |
针对请求,服务器可执行多种操作 |
|
301 |
永久移动 |
请求的网页永久移动到新的位置,即永久重定向 |
|
302 |
临时移动 |
请求的网页暂时跳转到其他页面,即暂时重定向 |
|
303 |
查看其他位置 |
如果原来的请求是POST,重定向目标文档应该通过GET提取 |
|
304 |
未修改 |
此次请求返回的网页未修改,继续使用上次的资源 |
|
305 |
使用代理 |
请求者应该使用代理访问该网页 |
|
307 |
临时重定向 |
请求的资源临时从其他位置响应 |
|
400 |
错误请求 |
服务器无法解析该请求 |
|
401 |
未授权 |
请求没有进行身份验证或者验证未通过 |
|
403 |
禁止访问 |
服务器拒绝此请求 |
|
404 |
未找到 |
服务器找不到请求的网页 |
|
405 |
方法禁用 |
服务器禁用了请求中指定的方法 |
|
406 |
不接受 |
无法使用请求的内容响应请求的网页 |
|
407 |
需要代理授权 |
请求者需要使用代理授权 |
|
408 |
请求超时 |
服务器请求超时 |
|
409 |
冲突 |
服务器在完成请求时发生冲突 |
|
410 |
已删除 |
请求的资源已永久删除 |
|
411 |
需要有效长度 |
服务器不接受不含有效内容长度标头字段的请求 |
|
412 |
未满足前提条件 |
服务器未满足请求者在请求中设置的其中一个前提条件 |
|
413 |
请求实体过大 |
请求实体过大,超出服务器的处理能力 |
|
414 |
请求URI过长 |
请求网址过长服务器无法处理 |
|
415 |
不支持类型 |
请求格式不被请求页面支持 |
|
416 |
请求范围不符 |
页面无法提供请求的范围 |
|
417 |
未满足期望值 |
服务器未满足期望值请求标头字段的要求 |
|
500 |
服务器内部错误 |
服务器遇到错误,无法完成请求 |
|
501 |
未实现 |
服务器不具备完成请求的功能 |
|
502 |
错误网关 |
服务器作为网关或者代理,从上游服务器收到无效响应 |
|
503 |
服务不可用 |
服务器目前无法使用 |
|
504 |
网关超时 |
服务器作为网关或者代理,但是没有及时从上游服务器收到请求 |
|
505 |
HTTP版本不支持 |
服务器不支持请求中所用的HTTP协议版本 |