德洛瓦:被弃之族免安装正式版
3.63G · 2025-10-22
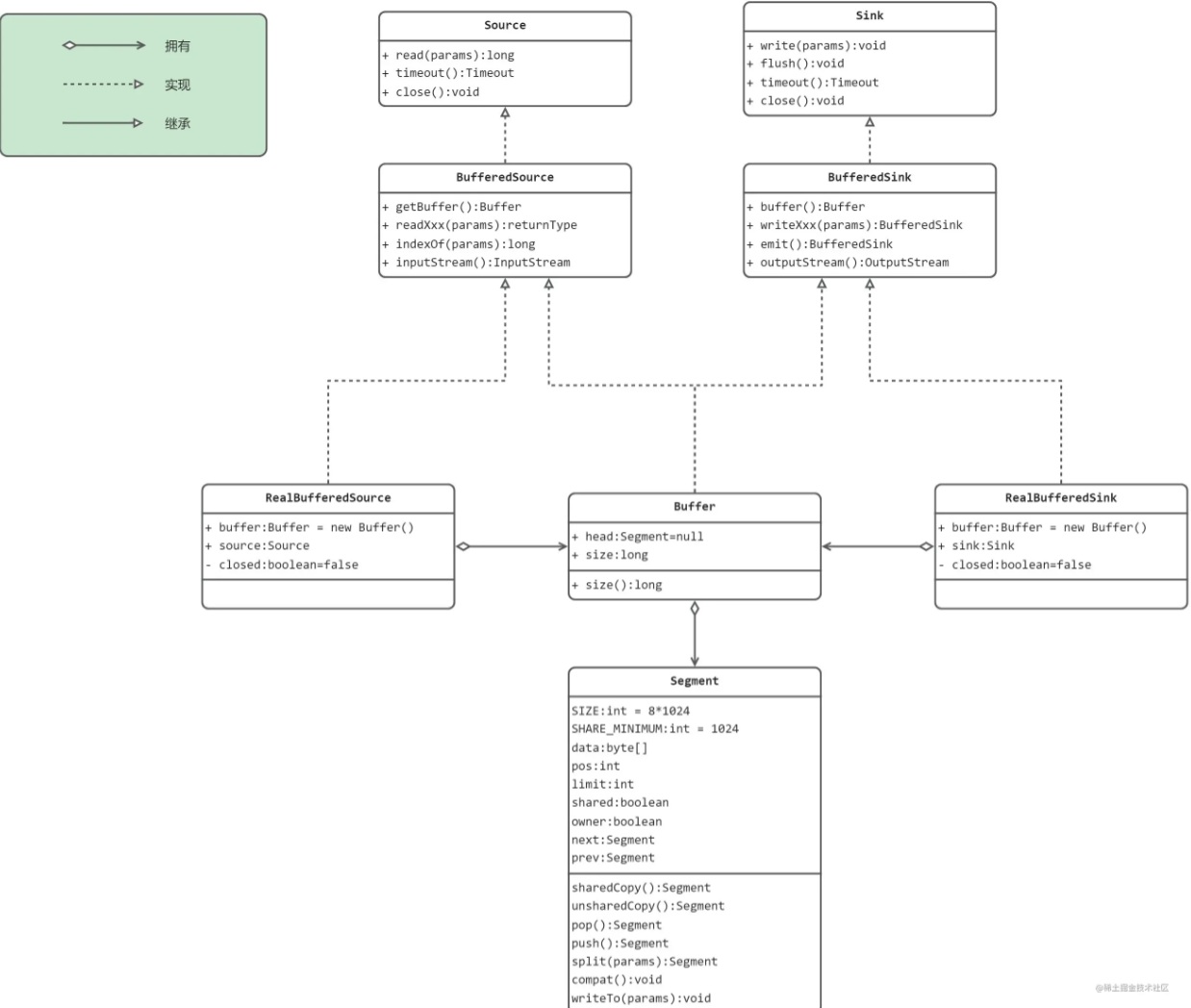
| 名称 | 类型 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| Source | 接口 | 定义了输入流的几个基本方法 |
| BufferedSource | 接口 | 继承Source接口,新增了一系列readXxx方法 |
| RealBufferedSource | 类 | 实现了BufferedSource接口 |
| Sink | 接口 | 定义了输出流的几个基本方法 |
| BufferedSink | 接口 | 继承Sink接口,新增了一系列writeXxx方法 |
| RealBufferedSink | 类 | 实现了BufferedSink接口 |
| Buffer | 类 | 同时实现了BufferedSource和BufferedSink接口。被RealBufferedSource和RealBufferedSink所持有,是读取和写入操作的真正实现类。 |
readXxx系列方法是从缓冲区读出数据的方法。writeXxx系列方法是向缓冲区写入数据的方法。使用 okio 来读取文件非常的简单,只需要简单的几步。
Okio.source方法获得Source对象Okio.buffer方法获得BufferedSource对象。因为BufferedSource是个接口,它里面定义了一系列的readXxx方法,可以用来方便的读取输入流的内容。public void readFile() {
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("test.txt");
okio.Source source = Okio.source(fis);
BufferedSource bs = Okio.buffer(source);
String res = bs.readUtf8();
System.out.println(res);
} catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}Okio.source重写了read方法,并返回一个Source对象。所以当我们调用**Source**对象的**read(Buffer sink, long byteCount)**方法时,其实是在调用该处重写的方法。read方法会从输入流进行一次读取操作,将数据读取到尾部的Segment中。
private static Source source(final InputStream in, final Timeout timeout) {
if (in == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("in == null");
if (timeout == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout == null");
return new Source() {
@Override public long read(Buffer sink, long byteCount) throws IOException {
if (byteCount < 0) throw new IllegalArgumentException("byteCount < 0: " + byteCount);
if (byteCount == 0) return 0;
try {
// 判断是否中断这次的读取操作
timeout.throwIfReached();
// 获取双链表尾部的 Segment
Segment tail = sink.writableSegment(1);
// 从输入流最多读取 maxToCopy 个字节
int maxToCopy = (int) Math.min(byteCount, Segment.SIZE - tail.limit);
// 从输入流读取数据到 Segment
int bytesRead = in.read(tail.data, tail.limit, maxToCopy);
// 到达输入流尾部
if (bytesRead == -1) return -1;
// 更新 tail 的 limit
tail.limit += bytesRead;
// 更新 sink 的 size 值
sink.size += bytesRead;
return bytesRead;
} catch (AssertionError e) {
if (isAndroidGetsocknameError(e)) throw new IOException(e);
throw e;
}
}
@Override public void close() throws IOException {
in.close();
}
@Override public Timeout timeout() {
return timeout;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "source(" + in + ")";
}
};
}read 方法首先会调用timeout.throwIfReached(),这个方法是Okio中的同步超时检测。它的作用有两个,一是检查当前线程是否中断,二是判断即将开始的读取操作是否在已经到达了截止时间,
 2025-10-22
2025-10-22
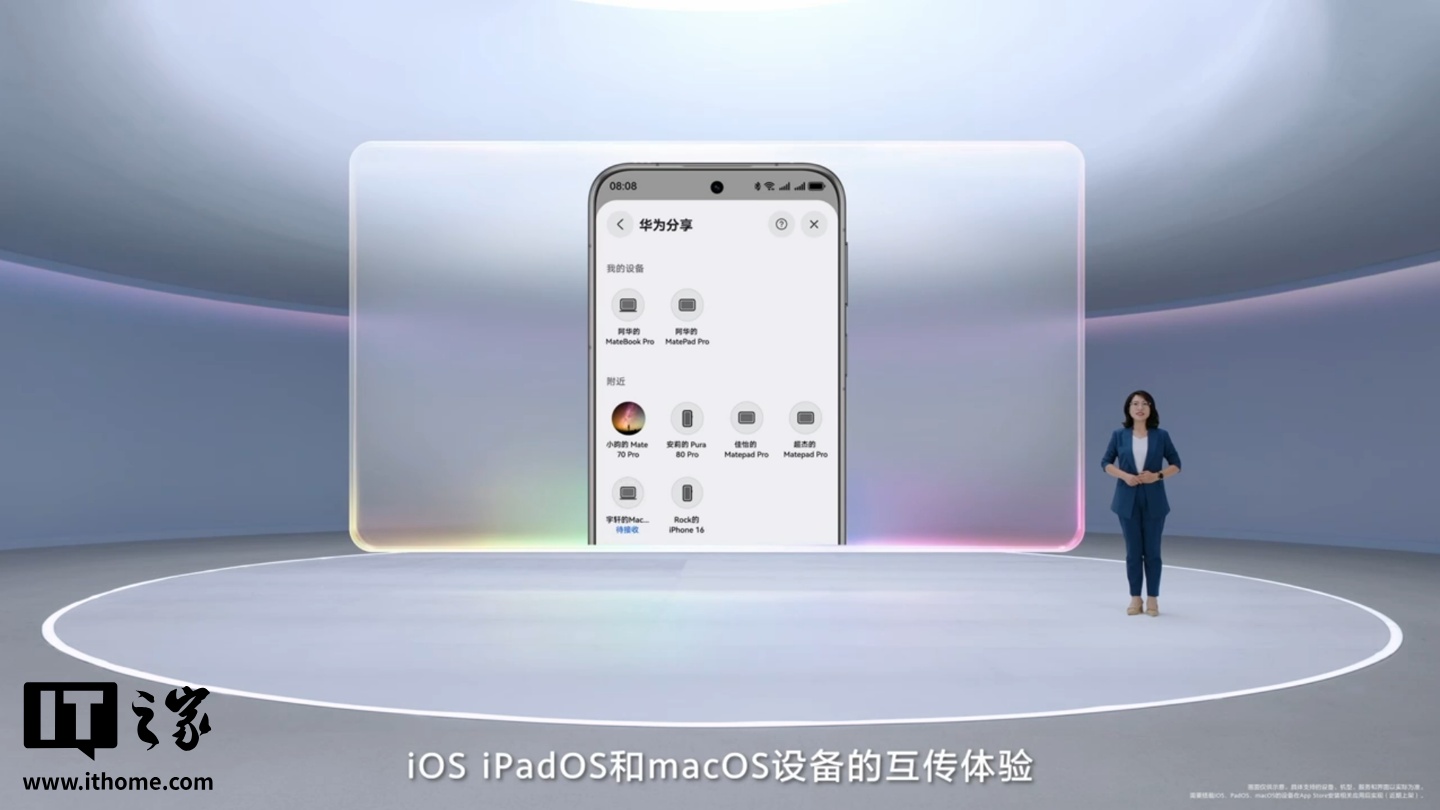
华为鸿蒙 HarmonyOS 6 支持与苹果 iOS / iPadOS / macOS 互传体验
 2025-10-22
2025-10-22
Netflix 宣布全力投入 AI:“能帮人类把故事讲得更好”